算法实现/排序/冒泡排序
外观
冒泡排序也称为涟漪排序。冒泡排序可能是任何初学者程序员必须编写的第一个比较复杂的模块。这是一个非常简单的构造,它向学生介绍了排序工作原理的基础知识。
冒泡排序使用一个数组和某种“交换”机制。大多数编程语言都有一个内置函数来交换数组元素。即使不存在交换函数,也只需要几行额外的代码来将一个数组元素存储在一个临时字段中,以便将第二个元素交换到它的位置。然后第一个元素从临时字段中移动,并回到数组中第二个元素的位置。
以下是如何进行冒泡排序的一个简单示例:假设你有一排带字母的儿童玩具积木。它们是随机排列的,你想按字母顺序从左到右排列它们。
- 步骤 1. 从第一个积木开始。在这种情况下,字母是G。(图 1)

图 1
- 步骤 2. 看看它右边的积木。
- 步骤 3. 如果右边的积木应该排在左边的积木之前,则交换它们,使它们按顺序排列(图 2)。

图 2
- 如果你是用手完成的,你可能只需要用一只手拿起要移动的积木,然后交叉手臂交换它们。或者你可以暂时将第一个积木移出其位置,将第二个积木移到其位置,然后将第一个积木移到现在为空的位置(这就是拥有一个单独函数来执行交换,还是编写一些代码来执行交换之间的区别)。
- 步骤 4. 将下一个积木与第一个积木比较,重复步骤 3. 直到你没有积木。然后从第二个积木开始再次执行步骤一。(图 3、4、5、6)

图 3 - 第 2 次遍历

图 4 - 第 3 次遍历
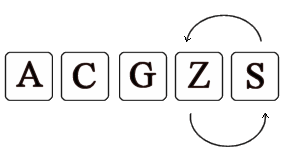
图 5 - 第 4 次遍历

图 6 - 排序完成
冒泡排序之所以得名,是因为元素倾向于像气泡升到水面一样上升到正确的位置。
CLS
DIM NameArray$(1000)
i = 0
' Seed read ...
READ Name$
' Loop through and read names in data ...
DO WHILE Name$ <> "*EOD"
i = i + 1
NameArray$(i) = Name$
READ Name$
LOOP
' The value of i is now the number of names in the array ...
ArraySize = i
' Bubble (or ripple) sort ...
FOR i = 1 TO ArraySize - 1
FOR j = 1 TO ArraySize - 1
IF NameArray$(j) > NameArray$(j + 1) THEN
SWAP NameArray$(j), NameArray$(j + 1)
END IF
NEXT j
NEXT i
' Print out the sorted results ...
FOR i = 1 TO ArraySize
PRINT NameArray$(i)
NEXT i
DATA Crowe,
DATA Adams,
DATA Zimmerman,
DATA Goodhead,
DATA Smith,
DATA Jones,
DATA *EOD
void BubbleSort (int a[], int length)
{
int i, j, temp;
for (i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < length - i - 1; j++)
{
if (a[j + 1] < a[j])
{
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
C++可以使用上面的 C 冒泡排序,或者针对通用容器的随机访问迭代器和通用比较运算符使用以下代码
#include <algorithm>
template<typename Iterator>
void bubbleSort(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
Iterator i, j;
for (i = first; i != last; i++)
for (j = first; j < i; j++)
if (*i < *j)
std::iter_swap(i, j); // or std::swap(*i, *j);
}
template<typename Iterator, class StrictWeakOrdering>
void bubbleSort(Iterator first, Iterator last, StrictWeakOrdering compare)
{
Iterator i, j;
for (i = first; i != last; i++)
for (j = first; j < i; j++)
if (compare(*i, *j))
std::iter_swap(i, j);
}
template <typename Iterator>
void bubbleSort(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
for (Iterator i, next; first != last; --last)
for (next = first, i = next, ++next; next != last; i = next, ++next)
if (*next < *i)
std::iter_swap(i, next);
}
template <typename Iterator, typename StrictWeakOrdering>
void bubbleSort(Iterator first, Iterator last, StrictWeakOrdering compare)
{
for (Iterator i, next; first != last; --last)
for (next = first, i = next, ++next; next != last; i = next, ++next)
if (compare(*next, *i))
std::iter_swap(i, next);
}
void bubbleSort(T)(T[] array) {
bool swapped;
T temp = void;
for (int j, i = array.length - 1; i; swapped = false, i--) {
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (array[j] > array[j+1]) {
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
if (!swapped) break;
}
}
static void BubbleSort(IComparable[] array)
{
int i = array.Length - 1;
while(i > 0)
{
int swap = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (array[j].CompareTo(array[j + 1]) > 0)
{
IComparable temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
swap = j;
}
}
i = swap;
}
}
static void BubbleSort<T>(IList<T> array) where T : IComparable<T>
{
int i, j;
T temp;
for (i = array.Count - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (array[j].CompareTo(array[j + 1]) > 0)
{
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
对整数数组进行排序。
type Integer_array is Array (Natural range <>) of Integer;
procedure Bubble_Sort (A : in out Integer_Array) is
Temp : Integer;
begin
for I in reverse A'Range loop
for J in A'First .. I loop
if A(I) < A(J) then
Temp := A(J);
A(J) := A(I);
A(I) := Temp;
end if;
end loop;
end loop;
end Bubble_Sort;
include io.h
.model small
.stack 200h
arrayLength equ 4
.data
str1 db 50 dup(?)
arrw dw arrayLength dup(?)
crlf db 10,13,0
.code
sort proc
for2:
s2: cmp [si],ax
jg big
jmp edame
big:
mov bx,[si]
mov [si],ax
mov [di],bx
edame:
cmp ax,0
jnz sd
jmp s0
sd:
add si,2
add di,2
mov ax,[di]
jmp edame2
s0:
mov si, offset arrw
mov di, si
add di,2
mov ax,[di]
edame2:
loop for2
ret
sort endp
Main proc
mov ax, @data
mov ds, ax
;---------------------------
mov si, offset arrw
mov cx, arrayLength
for1:
inputs str1,5
output crlf
atoi str1
mov [si], ax
add si, 2
loop for1
mov bx,arrayLength
while1: cmp bx,0
jbe endwhile1
mov si, offset arrw
mov di, si
add di,2
mov ax,[di]
mov cx,arrayLength
sub bx,1
call sort
jmp while1
endwhile1:
output crlf
mov si, offset arrw
mov cx, arrayLength
for3:
itoa str1,[si]
output crlf
output str1
add si,2
loop for3
;---------------------------
mov ax,4c00h
int 21h
Main endp
end Main
对变体数据类型的数组进行排序
Func BubbleSort(ByRef $bs_array)
For $i = UBound($bs_array) - 1 To 1 Step -1
For $j = 2 To $i
If $bs_array[$j - 1] > $bs_array[$j] Then
$temp = $bs_array[$j - 1]
$bs_array[$j - 1] = $bs_array[$j]
$bs_array[$j] = $temp
EndIf
Next
Next
Return $bs_array
EndFunc ;==>BubbleSort
Sub Bubblesort(Array() as Integer, Length as Integer)
Dim I as Integer
Dim J as Integer
Dim Temp as Integer
For I = Length -1 To 1 Step -1
For J = 0 to I - 1
IF Array(J)>Array(J+1) THEN ' Compare neighboring elements
Temp = Array(j)
Array(J) = Array(J+1)
Array(J+1) = Temp
End If
Next J
Next I
End Sub
BlitzBasic
[编辑 | 编辑源代码] unsorted=1
while unsorted
unsorted=0
for x = 1 to 10
if ar[x]<ar[x-1]
unsorted=1
tmp = ar[x]
ar[x] = ar[x-1]
ar[x-1] = tmp
end if
next
wend
(defun bubble-sort (lst)
(loop repeat (1- (length lst)) do
(loop for ls on lst while (rest ls) do
(when (> (first ls) (second ls))
(rotatef (first ls) (second ls)))))
lst)
(defun bubblesort (list pred)
"Sort LIST in order of comparison function PRED."
(let ((i (length list)))
(while (> i 1)
(let ((b list))
(while (cdr b)
(when (funcall pred (cadr b) (car b))
(setcar b (prog1 (cadr b)
(setcdr b (cons (car b) (cddr b))))))
(setq b (cdr b))))
(setq i (1- i)))
list))
SUBROUTINE sort (array_x, array_y, datasize)
Global Definitions
REAL array_x(*)
REAL array_y(*)
INTEGER datasize
Local
REAL x_temp
REAL y_temp
LOGICAL inorder
inorder = .false.
do 90 while (inorder.eq..false.)
inorder = .true.
do 91 i=1, (datasize-1)
Check Equilivant Points and swap those on Y
if (array_x(i).eq.array_x(i+1) ) then
if (array_y(i).lt.array_y(i+1) ) then
x_temp = array_x(i)
y_temp = array_y(i)
array_x(i) = array_x(i+1)
array_y(i) = array_y(i+1)
array_x(i+1) = x_temp
array_y(i+1) = y_temp
inorder = .false.
endif
endif
If x needs to be swapped, do so
if (array_x(i).lt.array_x(i+1) )then
x_temp = array_x(i)
y_temp = array_y(i)
array_x(i) = array_x(i+1)
array_y(i) = array_y(i+1)
array_x(i+1) = x_temp
array_y(i+1) = y_temp
inorder = .false.
endif
91 continue
90 continue
END SUBROUTINE sort
使用 sort 包的 Go 实现
func BubbleSort(list sort.Interface) {
for itemCount := list.Len() - 1; ; itemCount-- {
hasChanged := false;
for current := 0; current < itemCount; current++ {
next := current + 1
if list.Less(next, current) {
list.Swap(current, next)
hasChanged = true
}
}
if !hasChanged {
break
}
}
}
bubbleSort []=[]
bubbleSort x=
(iterate swapPass x) !! ((length x)-1)
where
swapPass [x]=[x]
swapPass (x:y:zs)
| x>y = y:swapPass (x:zs)
| otherwise = x:swapPass (y:zs)
public static int[] bubblesort(int[] numbers) {
boolean swapped = true;
for(int i = numbers.length - 1; i > 0 && swapped; i--) {
swapped = false;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (numbers[j] > numbers[j+1]) {
int temp = numbers[j];
numbers[j] = numbers[j+1];
numbers[j+1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
}
return numbers;
}
JavaScript
[编辑 | 编辑源代码]function bubbleSort (array) {
var temp;
do {
var newLocation = 0;
for(var i = 0, length = array.length; i < length - 1; ++i) {
if(arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {
/* swap */
temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
newLocation = i;
}
}
length = newLocation;
} while ( length );
}
为了简单起见,此版本在单独的步骤中检查更改。
let rec bsort s =
let rec _bsort = function
| x :: x2 :: xs when x > x2 ->
x2 :: _bsort (x :: xs)
| x :: x2 :: xs ->
x :: _bsort (x2 :: xs)
| s -> s
in
let t = _bsort s in
if t = s then t
else bsort t
Program BubbleSort:
const
MAXINTARRAY : 1000; { Set this value to fit your data needs for max array size }
STARTINTARRAY : 1; { Set 1 _or_ 0; indicates the lower index of the array }
Type
IntArray : Array[STARTINTARRAY..MAXINTARRAY] of integer;
(*===================================================================================
BubbleSort is an all purpose sorting procedure that is passed an array of
integers and returns that same array with the array elements sorted as desired.
Parameters are used to control the sorting operation:
If you want to sort the entire array, pass a value in Count that signals the number
of elements you want sorted. BubbleSort will then sort Count number of elements starting
with the first element in the array.
If you want to sort a subset of elements within the array, pass 0 in Count and pass
a beginning and ending subset index number in First and Last, respectively.
The sort will be either ascending or descending as controlled by the parameter Ascend:
Pass True in Ascend and the sort will be ascending. Pass False and the sort will be
descending.
Data: The array to be sorted.
NOTE: Sample is a var and will be modified by BubbleSort, unless the array is
already in a sorted state.
Count: 0 _or_ the number of elements to be sorted, starting with the first element.
First: The first element to be sorted in a subset of the array.
Last: The last element to be sorted in a subset of the array.
Ascend: Flag to indicate the sort order. True is ascending order. False is descending.
Succ: Flag returns result of BubbleSort
0 = success.
1 = Failed. Parameter First has value below allowed first index value.
2 = Failed. Parameter Last has value above allowed last index value.
3 = Failed. Parameter Last has value below allowed first index value.
===================================================================================*)
Procedure BubbleSort(
Var Data : IntArray;
Count : integer;
First : integer;
Last : integer;
Ascend : boolean;
Var Succ : integer );
var
i,
temp,
s_begin,
s_end,
numsort : integer;
sorted : boolean;
Begin
{ initialize for full array sort }
s_begin := STARTINTARRAY;
s_end := STARTINTARRAY + count - 1 ;
numsort := Count;
Succ := 0; { assume success }
{ check for a subset sort; check parameters for correctness }
if (Count = 0) then
Begin
If (First < STARTINTARRAY) then
Begin { error: sort start index too low }
Succ := 1;
Exit;
End;
If (Last > MAXINTARRAY) then
Begin { error: sort end index too high }
Succ := 2;
Exit;
End;
if (Last < STARTINTARRAY) then
Begin { error: sort end index too low }
Succ := 3;
Exit;
End;
s_begin := First;
s_end := Last;
numsort := Last - First + 1;
End;
If numsort <= 1 then Exit; { only one element, so exit }
If Ascend then
Begin { do the ascending sort }
Repeat
sorted := true; { flag default is true }
For i := s_begin to s_end -1 do
if (Data[i] < Data[i+1]) then
Begin
{ swap contents of Data[i] and Data[i+1] }
temp := Data[i];
Data[i] := Data[i+1];
Data[i+1] := temp;
{ set flag to indicate a swap occurred; i.e., sort may not be completed }
sorted := false;
End;
Until sorted;
End Else
Begin { do the descending sort }
Repeat
sorted := true; { flag default is true }
For i := s_begin to s_end -1 do
if (Data[i] < Data[i+1]) then
Begin
{ swap contents of Data[i] and Data[i+1] }
temp := Data[i];
Data[i] := Data[i+1];
Data[i+1] := temp;
{ set flag to indicate a swap occurred; i.e., sort may not be completed }
sorted := false;
End;
Until sorted;
End;
End;
简化版本
Procedure BubbleSort(var a:IntArray; size:integer);
var i,j,temp: integer;
begin
for i:=1 to size-1 do
for j:=1 to size do
if a[i]>a[j] then
begin
temp:=a[i]; a[i]:=a[j]; a[j]:=temp;
end;
end;
sub swap {
@_[ 0, 1 ] = @_[ 1, 0 ];
}
sub bubble_sort {
# returns a sorted copy
my (@a) = @_;
for my $i ( 0 .. $#a ) {
for my $j ( 0 .. $#a - 1 - $i) {
swap $a[$j], $a[ $j + 1 ]
if $a[$j] > $a[ $j + 1 ];
}
}
\@a;
}
function bubble_sort(sequence s)
object tmp
integer changed
for j=length(s) to 1 by -1 do
changed = 0
for i=1 to j-1 do
if s[i]>s[i+1] then
{s[i],s[i+1],changed} = {s[i+1],s[i],1}
end if
end for
if changed=0 then exit end if
end for
return s
end function
function bubbleSort ($items) {
$size = count($items);
for ($i=0; $i<$size; $i++) {
for ($j=0; $j<$size-1-$i; $j++) {
if ($items[$j+1] < $items[$j]) {
arraySwap($items, $j, $j+1);
}
}
}
return $items;
}
function arraySwap (&$arr, $index1, $index2) {
list($arr[$index1], $arr[$index2]) = array($arr[$index2], $arr[$index1]);
}
def bubblesort(lst):
"Sorts lst in place and returns it."
for passesLeft in range(len(lst)-1, 0, -1):
for index in range(passesLeft):
if lst[index] > lst[index + 1]:
lst[index], lst[index + 1] = lst[index + 1], lst[index]
return lst
0.up to(keys.size-1) do |i|
(i+1).up to(keys.size-1) do |j|
(keys[j], keys[j-1] = keys[j-1], keys[j]) if keys[j] <= keys[j-1]
end
end
puts keys
用于实现 Copy 和 PartialOrd 特征的泛型类型的 Rust 函数(例如数值类型或字符串)。
fn bubblesort<T: std::marker::Copy + std::cmp::PartialOrd>(arr: &mut [T]) -> &[T] {
let mut temp: T;
for i in 0..arr.len() {
for j in i..arr.len() {
if arr[i] > arr[j] {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
arr // return the sorted array
}
(define (bubblesort l)
(define (swap-pass l)
(if (NULL? l) ;to handle empty list
l
(let ((fst (car l))(snd (cadr l))(rest (cddr l)))
(if (> fst snd)
(cons snd (swap-pass (cons fst rest)))
(cons fst (swap-pass (cons snd rest)))))))
(let for ((times (length l))
(val l))
(if (> times 1)
(for (- times 1)(swap-pass val))
(swap-pass val))))
Standard ML
[编辑 | 编辑源代码]fun bubble_select [] lessThan =[]
| bubble_select [a] lessThan =[a]
| bubble_select (a::b::xs) lessThan =
if lessThan (b, a) then b::(bubble_select(a::xs) lessThan) else a::(bubble_select(b::xs) lessThan)
fun bubblesort [] lessthan =[]
| bubblesort (x::xs) lessthan =bubble_select (x::(bubblesort xs lessthan)) lessthan
Private Sub bubble(N as integer, array() as integer)
'N is the number of integers in the array'
'0 to N-1'
Dim I, J, P, Temp as Integer
For I = n - 1 To 0 Step -1
P=0
For J = 0 To I
If array(J) > array(J + 1) Then
Temp = array(J)
array(J) = array(J + 1)
array(J + 1) = Temp
Else
P=P+1
End If
If P=I then GoTo premend
Next J
Next I
'premend = premature ending = all integers are already sorted'
premend:
End Sub
请参见讨论以了解可能的错误。
Visual Basic
[编辑 | 编辑源代码] Public Sub BubbleSort(ByRef ArrayIn() As Long)
Dim i, j As Integer
For i = UBound(ArrayIn) To 0 Step -1
For j = 0 To i - 1
If ArrayIn(j) > ArrayIn(j + 1) Then
Call swap(ArrayIn(j), ArrayIn(j + 1))
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub
Private Sub swap(ByRef data1 As Long, ByRef data2 As Long)
Dim temp As Long
temp = data1
data1 = data2
data2 = temp
End Sub
global proc int[] SortList(int $list[])
{
int $i;
int $j;
int $temp;
int $flag;
int $n = `size($list)`;
for($i=$n-1; $i>0; $i--)
{
$flag = 1;
for($j=0; $i>$j; $j++)
{
if($list[$j]>$list[$j+1])
{
$flag = 0;
$temp = $list[$j];
$list[$j] = $list[$j+1];
$list[$j+1] = $temp;
}
}
if($flag) {
break;
}
}
return $list;
}
如果您要处理大量数据,请使用 COBOL SORT 通过顺序文件排序。对于排序 WORKING STORAGE 表,以下示例假设该表已加载。文字“a”指示行的大小,而“b”指示表中的行数。
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
*
01 WS-SORT-AREA.
05 WS-SORT-TABLE.
10 WS-SORT-ROW PIC X(''a'') OCCURS ''b''.
05 WS-TEMP-ROW PIC X(''a'').
05 WS-ROW-MAX PIC S9(4) COMP VALUE ''b''.
05 WS-SORT-MAX PIC S9(4) COMP.
05 WS-SORT-UP PIC S9(4) COMP.
05 WS-SORT-DOWN PIC S9(4) COMP.
05 WS-SORT-INCR PIC S9(4) COMP.
05 WS-SORT-TEST PIC S9(4) COMP.
*
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
*
MY-SORT SECTION.
MY-SORT-START.
*
* find the last entry
*
PERFORM VARYING WS-SORT-MAX FROM WS-ROW-MAX BY -1
UNTIL WS-SORT-MAX = ZERO
OR WS-SORT-ROW (WS-SORT-MAX) NOT = SPACES
END-PERFORM.
*
* bubble sort into required sequence
*
PERFORM VARYING WS-SORT-UP FROM WS-SORT-MAX BY -1
UNTIL WS-SORT-UP = ZERO
*
MOVE ZERO TO WS-SORT-TEST
*
PERFORM VARYING WS-SORT-DOWN FROM 1 BY 1
UNTIL WS-SORT-DOWN = WS-SORT-UP
*
ADD 1 TO WS-SORT-DOWN GIVING WS-SORT-INCR
*
IF WS-SORT-ROW (W30-SORT-DOWN)
> WS-SORT-ROW (W30-SORT-INCR)
*
MOVE WS-SORT-ROW (WS-SORT-DOWN)
TO WS-TEMP-ROW
MOVE WS-SORT-ROW (WS-SORT-INCR)
TO WS-SORT-ROW (WS-SORT-DOWN)
MOVE WS-TEMP-ROW
TO WS-SORT-ROW (WS-SORT-INCR)
ADD 1 TO WS-SORT-TEST
END-IF
END-PERFORM
*
IF WS-SORT-TEST = ZERO
NEXT SENTENCE
END-IF
END-PERFORM.
*
MY-SORT-EXIT.
EXIT.
