直角坐标系,或笛卡尔坐标系,是一种定位物体的方法。它是由一位名叫笛卡尔的数学家发明的。它类似于地理或计算机素养中的坐标系,但并不完全相同。
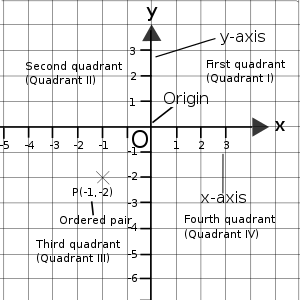
基本笛卡尔平面相关术语的概述 直角坐标系,或笛卡尔平面,由两条轴组成,即 x 轴和 y 轴。x 轴是水平轴,而 y 轴是垂直轴。这两条轴的交点称为原点,通常用字母 O 表示。在 x 轴和 y 轴上有刻度,它与统计图中的刻度非常相似,只是这里有负数。事实上,它们看起来像数轴,一条水平,一条垂直,并且它们的 '0' 点重合。
我们可以用有序对在坐标系中定位一个点。有序对由两个数字组成:即两个轴的读数。我们将 x 的读数放在前面,然后是 y,就像这样: (x, y)。坐标系被分成四个部分:第一象限 (象限 I)、第二象限 (象限 II)、第三象限 (象限 III) 和第四象限 (象限 IV)。四个象限的位置可以在右侧的图中找到。一个点可以位于这些象限中的任何一个、x 轴、y 轴或原点。我们可以通过观察点的坐标来找出有序对的一些基本性质。
象限 I: (x , y )
象限 II: (-x , y )
象限 III: (-x , -y )
象限 IV: (x , -y )
x 轴: (x 或 -x , 0)
y 轴: (0, y 或 -y )
原点: (0, 0) 在确定点的有序对时,请记住,刻度不一定是 1 对 1 的。这意味着数字不必按照 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 的顺序排列。它们也可以按照 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 甚至 5, 10, 15, 20 的顺序排列。
如果你完全确定两个点构成一条水平线或垂直线,水平线的定义是平行于 x 轴,垂直线的定义是平行于 y 轴,那么你可以参考另一个点,在没有刻度的帮助下找到一个点或两个点的坐标。例如,如果 P (3, 4) 与 Q (3, y ) 位于同一条垂直线上,那么 y = 4。
我们用一个复杂的问题来介绍下一部分(见右侧的图)。
求
QP 的长度所有阴影区域的面积之和
如果 F : (-2, -3),求 I 的坐标 乍一看有点复杂,所以我们先从第一象限的直线 QP 开始,这条线看起来比较容易。如果可以,我们将计算出所有未知数,并解决第一个目标。首先,让我们看一下 P 的坐标。它们是 (1, 2)。由于 P 和 Q 位于同一条水平线上,所以它们的 y 坐标必须相同。因此,Q 的坐标必须是 (3, 2)。换句话说,z = 2。要找到 PQ 的长度,我们只需找到它们 x 坐标的差;在本例中,3 - 1 = 2 个单位。因此,QP = 2 个单位。在数学表示中,这将是
∵ The y -coordinate of P = 2 ∴ z = 2 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\because {\text{The }}y{\text{-coordinate of }}P=2\\\therefore z=2\end{aligned}}}
The length of P Q = 3 − 1 = 2 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The length of }}\ PQ&=3-1\\&=2{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}
很好!现在我们已经解决了第一个目标,让我们继续处理第二象限的小三角形。同样,我们将计算出所有未知数。首先,让我们看一下 C 的 x 坐标。我们已经知道 z = 2,所以 -z 必须是 -2,因此 C 的 x 坐标也是 -2。那么 y 坐标呢?我们知道 B 和 C 位于同一条水平线上,所以它们的 y 坐标必须相同。因此,C 的 y 坐标也必须是 1,并且 y = 1。B 的 x 坐标,称为 x ,也是未知的。由于 A 和 B 位于同一条垂直线上,所以它们的 x 坐标必须相同。因此,我们可以推断 x = -4。在数学表达式中
The x -coordinate of C = − z = 1 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The }}\ x{\text{-coordinate of }}\ C&=-z\\&=1\end{aligned}}}
∵ The y -coordinate of B = 1 ∴ y = 1 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\because {\text{The }}y{\text{-coordinate of }}B=1\\\therefore y=1\end{aligned}}}
∵ The x -coordinate of A = − 4 ∴ x = − 4 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\because {\text{The }}x{\text{-coordinate of }}A=-4\\\therefore x=-4\end{aligned}}}
接下来,我们将找出三角形ABC的面积。这在寻找阴影区域的总面积时将非常有用。在我们这样做之前,我们必须找出三角形的高度和底边。你还记得三角形面积公式吗?它是高度乘以底边除以二。让我们选择BC作为三角形的底边。由于AB和BC相互垂直,AB可以作为高度。由于BC是水平的,BC的长度是B和C的x坐标之差。那就是-4和-1,所以BC的长度是[(-1)-(-4)]个单位=3个单位。对于AB,情况相反。由于AB是一条垂直线,我们应该找出它们的y坐标之差。在这种情况下,那就是(3-1)个单位=2个单位。因此,三角形ABC的面积是(3-2)平方单位=1平方单位。让我们看看数学表达式中的情况。
The length of B C = x − ( − z ) units = [ ( − 1 ) − ( − 4 ) ] units = 3 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The length of }}\ BC&=x-(-z){\text{ units}}\\&=[(-1)-(-4)]{\text{ units}}\\&=3{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}
The length of A B = 3 − 1 units = 2 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The length of }}\ AB&=3-1{\text{ units}}\\&=2{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}
The area of △ A B C = B C × A B 2 sq. units = 3 × 2 2 sq. units = 3 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The area of }}\ \triangle ABC&={\frac {BC\times AB}{2}}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&={\frac {3\times 2}{2}}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&=3{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}
现在我们只需要算出两个底部象限中图形的面积。该图形的形状像一个梯形,一边粘着一个三角形,中间有一个洞。利用我们之前学到的知识,你应该能够算出a=-4,b=-6。请注意,我们已经从上面知道了-z的值,它是-2。现在我们必须找到梯形、三角形和正方形孔的面积。让我们先算出三角形的面积。从Z画一条虚线垂直于XY,并将其命名为R。R的坐标是(-4,-5),参考点X和Z。ZR和XY的长度应该是1和4,所以三角形XYZ的面积一定是2平方单位。详细信息如下所示的数学表达式。
∵ The x -coordinate of X = − 4 ∴ a = − 4 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\because {\text{The }}x{\text{-coordinate of }}X=-4\\\therefore a=-4\end{aligned}}}
∵ The y -coordinate of Y = − 6 ∴ b = − 6 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\because {\text{The }}y{\text{-coordinate of }}Y=-6\\\therefore b=-6\end{aligned}}}
The y -coordinate of D = − z = − 2 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The }}y{\text{-coordinate of }}D=-z\\=-2\end{aligned}}}
The length of Z R = ( − 5 ) − ( − 4 ) units = 1 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The length of }}\ ZR&=(-5)-(-4){\text{ units}}\\&=1{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}
The length of X Y = ( − 2 ) − ( − 6 ) units = 4 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The length of }}\ XY&=(-2)-(-6){\text{ units}}\\&=4{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}
The area of △ X Y Z = Z R × X Y 2 sq. units = 1 × 4 2 sq. units = 2 sq. units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The area of }}\ \triangle XYZ&={\frac {ZR\times XY}{2}}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&={\frac {1\times 4}{2}}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&=2{\text{ sq. units}}\end{aligned}}}
现在我们需要找到直角梯形的面积。你还记得梯形面积公式吗?它是平行线之和乘以高,再除以2。我们需要找到平行线的长度和高度才能找到面积。我们已经知道高度 _XY_。_XD_ 和 _YE_ 的长度分别为9和8,所以梯形的面积为34平方单位。具体细节如下。
The length of X D = ( − 4 ) − 5 units = 9 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The length of }}\ XD&=(-4)-5{\text{ units}}\\&=9{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}
The length of Y E = ( − 4 ) − 4 units = 4 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The length of }}\ YE&=(-4)-4{\text{ units}}\\&=4{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}
The area of trapezium X Y D E = ( X D + Y E ) × X Y 2 sq. units = ( 9 + 4 ) × 4 2 sq. units = 26 sq. units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The area of trapezium}}\ XYDE&={\frac {(XD+YE)\times XY}{2}}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&={\frac {(9+4)\times 4}{2}}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&=26{\text{ sq. units}}\end{aligned}}}
下一步是找到正方形的面积。正方形的公式是边长的平方,所以正方形 _FGHI_ 的面积是 _z_2 = 22 单位 = 4 单位。
The area of square F G H I = F I 2 sq. units = z 2 sq. units = 2 2 sq. units = 4 sq. units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The area of square}}\ FGHI&=FI^{2}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&=z^{2}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&=2^{2}{\text{ sq. units}}\\&=4{\text{ sq. units}}\end{aligned}}}
第二点的最后部分是利用我们在前面章节中学到的关于平面形状的知识来计算阴影区域的总面积。首先要找到第三和第四象限图形的总面积。第三和第四象限的阴影面积 = 五边形 XZYED 的面积 - 正方形 FGHI 的面积 = 三角形 XYZ 的面积 + 梯形 XYDE 的面积 - 正方形 FGHI 的面积 = (2+26-4) 平方单位 = 24 平方单位。接下来,我们将它添加到三角形 ABC 的面积,得到 (24+3) 平方单位 = 11 平方单位。数学表达式如下所示。
The shaded area in quadrants III and IV = Area of △ X Y Z sq. units + Area of trapezium X Z Y E D − Area of square F G H I = ( 2 + 26 − 4 ) sq. units = 24 sq. units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}&{\text{The shaded area in quadrants III and IV }}\\&={\text{Area of }}\triangle XYZ{\text{ sq. units}}+{\text{Area of trapezium }}XZYED-{\text{Area of square }}FGHI\\&=(2+26-4){\text{ sq. units}}\\&=24{\text{ sq. units}}\end{aligned}}}
所有阴影区域的总和 = ( 24 + 3 ) 平方单位 = 27 平方单位 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The sum of all shaded areas }}&=(24+3){\text{ sq. units}}\\&=27{\text{ sq. units}}\end{aligned}}}
由于我们已经完成了两个目标,现在是时候找到第三个目标了。第三个目标需要一种与我们上面使用的技术相反的技术。您可能已经注意到,第三个目标与其他目标不同,它需要找到坐标,而不是度量。请记住,我们从问题中知道的唯一坐标是点F 的坐标。还要记住,正方形的四条边都相等。由于我们可以根据线段端点的坐标找到线段的长度,因此我们可以根据线段的长度找到端点的坐标。
那么,我们到底要怎么做呢?F 的坐标是 (-2, -3)。我们可以找到I 的y 坐标,我们已经知道它与F 的y 坐标相同。因此,y 坐标是 -3。但是x 坐标呢?由于我们知道FI = z = 2 个单位,我们可以算出I 的x 坐标为 [(-2)+2)] 个单位 = 4 个单位。请记住,我们要找的端点的坐标相对于已经知道的端点的坐标位置很重要。如果I 位于F 的右侧,而不是左侧,则它的x 坐标将为 [(-2)-2)] 个单位 = -4 个单位。如果I 位于F 的上方或下方,它们的x 坐标将相同,而I 的y 坐标将为 [(-3)-2)] 个单位 = -5 个单位(下方)或 [(-3)+2)] 个单位 = -1 个单位(上方)。
∵ The y -coordinate of F = − 3 ∴ The y -coordinate of I = − 3 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\because {\text{The }}y{\text{-coordinate of }}F=-3\\\therefore {\text{The }}y{\text{-coordinate of }}I=-3\end{aligned}}}
∵ F I = z = 2 units {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\because FI=z\\=2{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}} ∴ The x -coordinate of I = [ ( − 2 ) + 2 ) ] = 4 {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\therefore {\text{The }}x{\text{-coordinate of }}I=[(-2)+2)]\\&=4\end{aligned}}}
就是这样!我们不仅学习了如何在矩形坐标系中找出形状的长度和面积以及点的坐标,还看到了一个重要的例子,说明了如何计算面积。







![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{The length of }}\ BC&=x-(-z){\text{ units}}\\&=[(-1)-(-4)]{\text{ units}}\\&=3{\text{ units}}\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9ed707e08315fbae43e73fe3df868022c03d38b7)
















![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\therefore {\text{The }}x{\text{-coordinate of }}I=[(-2)+2)]\\&=4\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3a56cf9a7a5b74462fa93f938d0c4c785f52b77f)