使用 C 和 C++ 的编程语言概念/异常处理
C 中的异常和错误处理,如果有的话,是通过特殊返回值来完成的,这些返回值不能由函数调用的正常完成产生。例如,考虑 printf 或它的其中一个朋友。如果一切正常,对这些函数的调用通常会返回发送到输出流的字符数。如果出现错误,EOF[1] 会被返回 - 这是一个在一切正常的情况下永远不会被返回的值。
或者,假设你实现了一个函数,该函数查找容器中特定项目的出现次数。这通常意味着返回零或一个正整数。如果容器不存在,并且你想将其作为反馈提供,该怎么办?返回零没有帮助;这意味着容器中没有项目。一个正值也无济于事。返回一个负值,比如 -1 怎么样?
这回答了我们对处理异常情况的担忧。但是,根据规范编写代码不会很有趣。考虑以下代码片段,其中程序员尽其所能为每个函数调用提供控制。
... ret = f(...); if (ret < 0) { if (ret == RETF_ABNORMAL_1) do-something-1; else if (ret == RETF_ABNORMAL_2) do-something-2; ... else do-something-n; } /* end of if (ret < 0)*/ ... ret = g(...); if (ret != NO_ERROR) { ... ... } /* end of if (ret != NO_ERROR) */ ...
看起来很乱,对吧?弄清楚控制流是一项难以忍受的任务,需要遍历无数的 if 和 else-if。代码充斥着错误处理代码,这使得维护人员难以维护。[2] 它几乎让你认为情况不会更糟。
如果我们能够保证程序无故障,上面的代码将缩减为两行,并且更容易阅读和理解。或者,如果我们能够将错误处理代码与其他代码隔离,那将非常棒。这正是许多语言中找到的异常处理机制所做的:隔离处理意外条件的代码部分,以便更轻松地维护程序。
然而,在 C 中这是不可能的。在 C 中,你必须要么走众所周知的路径[并用无数个 if 和 else-if 填充你的代码],要么使用 setjmp-longjmp 对。在本讲义中,我们将看看后者,并介绍两个互补的概念,断言和信号。
但是,在我们继续之前 - 为了给异常处理机制的内部工作提供一些启发 - 我们将简单介绍一下 Win32 操作系统中是如何处理异常的。[3]
Win32 中的异常处理的基础是异常的注册。这是通过将异常记录插入到一个链接结构中来完成的,该结构的第一个节点由 FS:[0] 指向;当 try-catch 块进入和退出时,分别插入和删除新记录。
为了简单起见,编译(并链接)以下 C 程序并运行可执行文件。[4]
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
DWORD scratch = 2;
下一个函数包含对 EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION 的处理代码,这意味着线程尝试访问一些无法访问的内存。这可能是由于尝试写入内存的只读部分或从没有相应权限的区域读取造成的。由于此异常是通过将一些有效地址值移入 EAX 来处理的,因此我们使用 ExceptionContinueExecution 返回,这意味着将再次尝试生成异常的指令。
如果抛出的异常不是 EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION,则通过返回 ExceptionContinueSearch 将控制权转移到列表中的下一个处理程序。
struct _CONTEXT,不出所料,是一个依赖于 CPU 的结构,它由包含机器状态的字段组成,而 ContextRecord 用于保存异常发生时所做的快照。与其相辅相成的是一个独立于 CPU 的结构,其中包含有关最近发生的异常的信息,例如它的类型、发生异常的指令地址等等。当发生异常时,操作系统将这些结构以及一个包含指向它们的每个结构的指针的第三个结构推送到引发异常的线程的堆栈上。
EXCEPTION_DISPOSITION __cdecl av_handler(
struct _EXCEPTION_RECORD *ExcRec,
void* EstablisherFrame,
struct _CONTEXT *ContextRecord,
void* DispatcherContext) {
printf("In the handler for ACCESS_VIOLATION\n");
if (ExcRec->ExceptionCode == EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION) {
ContextRecord->EAX = (DWORD) &scratch;
printf("Handled access violation exception...\n");
} else {
printf("Cannot handle exceptions other than acc. violation!\n");
printf("Moving on to the next handler in the list\n");
return ExceptionContinueSearch;
}
return ExceptionContinueExecution;
} /* end of EXCEPTION_DISPOSITION av_handler(.....) */
这是我们的第二个处理程序函数,它处理[整数]除以零异常。代码没有新东西!
不过,值得一提的是:处理程序函数可以合并成一个。没有规定说每个异常都必须有自己的处理程序函数。在我们的例子中,以下函数也能达到目的。
EXCEPTION_DISPOSITION __cdecl common_handler( struct _EXCEPTION_RECORD *ExcRec, void* EstablisherFrame, struct _CONTEXT *ContextRecord, void* DispatcherContext) { printf("In the shared handler\n"); if (ExcRec->ExceptionCode == EXCEPTION_INT_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO) { printf("Handled divide by zero exception...\n"); ContextRecord->EBX = (DWORD) scratch; } else if (ExcRec->ExceptionCode == EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION) { ContextRecord->EAX = (DWORD) &scratch; printf("Handled access violation exception...\n"); } else { printf("Cannot handle exceptions other than div. by zero and acc. violation\n"); printf("Moving on to the next handler in the list\n"); return ExceptionContinueSearch; } return ExceptionContinueExecution; } /* end of EXCEPTION_DISPOSITION common_handler(.....) */ ... DWORD sole_handler = (DWORD) &common_handler; ...
EXCEPTION_DISPOSITION __cdecl dbz_handler(
struct _EXCEPTION_RECORD *ExcRec,
void* EstablisherFrame,
struct _CONTEXT *ContextRecord,
void* DispatcherContext) {
printf("In the handler for INT_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO\n");
if (ExcRec->ExceptionCode == EXCEPTION_INT_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO) {
printf("Handled divide by zero exception...\n");
ContextRecord->EBX = (DWORD) scratch;
} else {
printf("Cannot handle exceptions other than div. by zero\n");
printf("Moving on to the next handler in the list\n");
return ExceptionContinueSearch;
}
return ExceptionContinueExecution;
} /* end of EXCEPTION_DISPOSITION dbz_handler(.....) */
int main(void) {
DWORD handler1 = (DWORD) &av_handler;
DWORD handler2 = (DWORD) &dbz_handler;
以下汇编代码块为可能的异常注册了处理程序。它通过将 _EXCEPTION_REGISTRATION_RECORD(一个用于访问冲突,另一个用于除零错误)插入到用于保存有关异常处理程序信息的链接列表的头部来实现这一点。这个 [异常注册] 结构有两个字段:一个指向先前结构的指针,即列表中的下一个节点,以及一个指向回调函数的指针,该函数在异常发生时被调用。
这几乎是 Win32 编译器在进入 `try` - `block` 时生成的代码片段:它将相关 `catch` 块的代码注册为 `handlers2`,方法是将它们添加到一个列表的头部,该列表的第一个项目由 `FS:[0]` 中的值指向。在完成 `try` 块后,在入口处注册的任何处理程序都将从列表中删除。
__asm {
PUSH handler1 ; push address of av_handler
PUSH FS:[0]
MOV FS:[0], ESP
PUSH handler2 ; push address of dbz_handler
PUSH FS:[0]
MOV FS:[0], ESP
}
当控制到达这里时,与异常处理相关的内存部分图像将如下所示。[5] 从 `av_handler` 记录中发出的指针指向默认处理程序,该处理程序将被调用来处理任何未处理的异常。
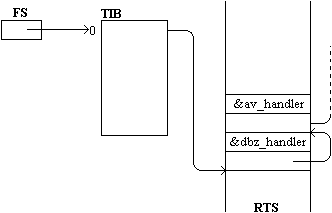
接下来,我们尝试将 1 存储到一个 4 字节的内存区域中,该区域的起始地址包含在 `EAX` 中。但是,我们的尝试将导致一个异常,因为 `EAX` 包含 0,并且地址 0 对 Win32 系统中的进程来说是禁区。[6]
__asm {
MOV EAX, 0
MOV [EAX], 1
}
__asm {
MOV EAX, 6
MOV EDX, 0
MOV EBX, 0
DIV EBX
}
下一个汇编代码块删除了在进入 `main` 时插入的异常记录。[7] 这与 Win32 编译器在退出 `try` - `catch` 块时生成的代码大致相同。
__asm {
MOV EAX, [ESP]
MOV FS:[0], EAX
ADD ESP, 8
MOV EAX, [ESP]
MOV FS:[0], EAX
ADD ESP, 8
}
printf("Will intentionally try dividing by zero once more!\n");
现在 `dbz_handler` 已从列表中删除,在以下代码块中抛出的除零错误异常将由默认处理程序(即 `UnhandledExceptionFilter` 系统函数)处理,该函数只是显示一个众所周知的、最烦人的消息框。</syntaxhighlight>
__asm {
MOV EAX, 6
MOV EDX, 0
MOV EBX, 0
DIV EBX
}
return 0;
} /* end of int main(void) */
- cl /w /FeExcTest.exe Exc_Test.c /link /SAFESEH:NO↵
- ExcTest↵
- In the handler for INT_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO
- Cannot handle exceptions other than div. by zero
- Moving on to the next handler in the list
- In the handler for ACCESS_VIOLATION
- Handled access violation exception...
- Handled divide by zero exception...
- Will intentionally try dividing by zero once more!
使用 Microsoft 扩展在 C 中进行异常处理
[edit | edit source]使用 Microsoft 扩展,您可以编写具有异常处理功能的 [不可移植的] C 程序,尽管方式略有不同。以下是一个简单的例子。
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int *iptr = 0;
int zero = 0;
int res;
以下是一个异常过滤器函数的例子。 _EXCEPTION_FILTER_ 决定在发生异常时要采取什么行动。在这样做时,它可以根据异常的类型做出不同的反应。例如,我们的过滤器函数在发生访问冲突异常时提供了一些补救措施,而对于其他类型的异常,它将决策推迟到列表中的下一个处理程序。
LONG av_filter(DWORD exc_code) {
if (exc_code == EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION) {
printf(“In the handler for ACCESS_VIOLATION\n”);
iptr = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
*iptr = 0;
printf(“Handled access violation exception...”);
return EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_HANDLER;
} else return EXCEPTION_CONTINUE_SEARCH;
} /* end of LONG av_filter(DWORD) */
int main(void) {
类似于编程语言级别提供的结构,Microsoft SEH 有 _GUARDED REGION_(`__try`)的概念,它后面是 _HANDLER CODE_(`__except` 或 `__finally`)。一个主要区别是处理程序的数量:在 SEH 中,可以在一个特定的 `__try` 后面使用 `__except` 或 `__finally` 中的任意一个,并且只能使用一次。
在执行受保护区域之前,相关的处理程序行(18 到 22 行)通过编译器合成的代码向操作系统注册,这与上一节的 39 到 46 行大致相同。在此之后,受保护区域被执行并导致异常,该异常通过传递给 `__except` 的表达式进行过滤。在我们的例子中,过滤器决定如果这是一个除零异常,则继续执行当前处理程序;否则,它将决策推迟到列表中的下一个处理程序。
当控制到达第 23 行时,由于编译器合成的代码,同一个处理程序将被取消注册,这与上一节的 57 到 64 行大致相同。
__try { res = 2 / zero; }
__except(GetExceptionCode() == EXCEPTION_INT_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO ? EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_HANDLER : EXCEPTION_CONTINUE_SEARCH) {
printf(“Knew this would happen...”);
res = 3;
}
printf(“ res: %d\n”, res);
下一个 `__except` 不是一个简单的过滤器,而是一个过滤器函数,它具有完全相同的功能。
__try { *iptr = 0; }
__except(av_filter(GetExceptionCode())) { }
printf(“ *iptr: %d\n”, *iptr);
free(iptr);
由于所有用户编写的处理程序都被拉了下来,因此执行第 29 行导致的异常将由操作系统提供的 _默认处理程序_ 处理,该处理程序负责处理所有未处理的异常。
printf(“Will intentionally try dividing by zero once more!\n”);
res = 2 / zero;
return 0;
} /* end of int main(void) */
- cl /FeExcSEH.exe Exc_SEH.c↵
- ExcSEH↵
- ...
- ...
- ...
模块
[edit | edit source]接口
[edit | edit source]#ifndef LIST_H
#define LIST_H
以下指令是必需的,它引入类型定义和函数原型,以便进行跨函数边界跳转。除了 `setjmp` 和 `longjmp` 的原型之外,该头文件还包含用于缓冲区类型的定义,该类型实例用于在上述函数之间进行通信。
#include <setjmp.h>
#include "General.h"
#include "ds/ListIterator.h"
struct LIST;
typedef struct LIST* List;
typedef struct _Object_funcs {
COMPARISON_FUNC compare_component;
COPY_FUNC copy_component;
DESTRUCTION_FUNC destroy_component;
} List_Component_Funcs;
typedef enum {ITERATOR_BACKWARD, ITERATOR_FORWARD} Iterator_type;
#define EXC_LIST_EMPTY -21
#define FROM_ARRAY 2
extern List List_Create(int constructor_type, ...);
extern void List_Destroy(List*);
`jmp_buf` 是一个机器相关的[8] 缓冲区,用于保存程序状态信息。我们所做的基本上是在执行可能产生异常的代码块之前填充该缓冲区,并且如果抛出异常,则使用其中找到的值来产生执行代码块之前存在的环境。
extern Object List_GetFirst(const List this, jmp_buf get_first_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty */ ;
extern Object List_GetLast(const List this, jmp_buf get_last_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty */ ;
extern void List_InsertAtEnd(const List, Object new_item);
extern void List_InsertInFront(const List, Object new_item);
extern Object List_RemoveFromEnd(const List this, jmp_buf rmv_from_end_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty */ ;
extern Object List_RemoveFromFront(const List this, jmp_buf rmv_from_front_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty */ ;
extern BOOL List_IsEmpty(const List);
extern int List_Size(const List);
extern List List_Merge(const List, const List otherList);
extern Object* List_ToArray(const List this, jmp_buf to_array_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty */ ;
extern ListIterator List_ListIterator(const List, Iterator_type it_type);
#endif
#ifndef LISTEXTENDED_H
#define LISTEXTENDED_H
#include <setjmp.h>
#include "General.h"
#include "ds/List.h"
#define EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM -26
extern void List_InsertAfterFirst(const List, Object, Object, jmp_buf ins_after_first_caller)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_InsertAfterLast(const List, Object, Object, jmp_buf ins_after_last_caller)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_InsertAfterNth(const List, Object, Object, int, jmp_buf ins_after_Nth_caller)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_InsertBeforeFirst(const List, Object, Object, jmp_buf ins_before_first_caller)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_InsertBeforeLast(const List, Object, Object, jmp_buf ins_before_last_caller)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_InsertBeforeNth(const List, Object, Object, int, jmp_buf ins_before_Nth_caller)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_InsertInAscendingOrder(const List, Object);
extern void List_InsertInAscendingOrderEx(const List, Object, COMPARISON_FUNC);
extern void List_InsertInDescendingOrder(const List, Object);
extern void List_InsertInDescendingOrderEx(const List, Object, COMPARISON_FUNC);
extern int List_RemoveAll(const List, Object, jmp_buf rmv_all_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty */ ;
extern void List_RemoveFirst(const List, Object, jmp_buf rmv_first_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty, NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_RemoveLast(const List, Object, jmp_buf rmv_last_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty, NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_RemoveNthFromEnd(const List, Object, int, jmp_buf rmv_Nth_from_end_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty, NoSuchItem */ ;
extern void List_RemoveNthFromFront(const List, Object, int, jmp_buf rmv_Nth_from_front_caller)
/* throws ListEmpty, NoSuchItem */ ;
#endif
#ifndef LISTITERATOR_H
#define LISTITERATOR_H
#include <setjmp.h>
#include "General.h"
#define EXC_ITERATOR_ILLEGALSTATE -31
#define EXC_ITERATOR_ILLEGALARGUMENT -32
#define EXC_ITERATOR_NOSUCHELEMENT -33
#define EXC_ITERATOR_UNSUPPORTEDOPERATION -34
struct LISTITERATOR;
typedef struct LISTITERATOR* ListIterator;
extern void ListIterator_Destroy(ListIterator*);
extern BOOL ListIterator_HasNext(const ListIterator);
extern Object ListIterator_Next(const ListIterator, jmp_buf next_caller)
/* throws NoSuchElement */ ;
extern int ListIterator_NextIndex(const ListIterator);
extern BOOL ListIterator_HasPrevious(const ListIterator);
extern Object ListIterator_Previous(const ListIterator, jmp_buf prev_caller)
/* throws NoSuchElement */ ;
extern int ListIterator_PreviousIndex(const ListIterator);
extern void ListIterator_Remove(const ListIterator, jmp_buf rmv_caller)
/* throws IllegalState, UnsupportedOperation */ ;
extern void ListIterator_Add(const ListIterator, Object, jmp_buf add_caller)
/* throws IllegalState, UnsupportedOperation */ ;
extern void ListIterator_Set(const ListIterator, Object, jmp_buf set_caller)
/* throws IllegalArgument, IllegalState, UnsupportedOperation */ ;
#endif
实现
[edit | edit source]#include <setjmp.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "General.h"
#include "ds/ListExtended.h"
#include "ds/ListIterator.h"
#define IT_OPERATION_NOOP 0
#define IT_OPERATION_ADD 1
#define IT_OPERATION_NEXT 2
#define IT_OPERATION_PREVIOUS 3
#define IT_OPERATION_REMOVE 4
#define IT_OPERATION_SET 5
似曾相识:一个指向某些元数据的句柄,该元数据又包含一个指向容器的指针,该容器保存集合的组件。

当您设计集合时,这种重复模式是一个很好的起点。句柄的存在是为了防止用户直接操作数据结构,并且对于维护也很有用,因为它占用恒定的内存量;元数据用于保存有关结构的或/和结构的属性的状态信息;容器用于物理地保存数据。
观察到我们使用了尚未定义的类型(struct _LIST)。编译器对此没有任何抱怨,因为我们没有使用类型本身,而是使用了指向该类型的指针,而该指针的大小是已知的。
struct LIST {
COMPARISON_FUNC compare_component;
COPY_FUNC copy_component;
DESTRUCTION_FUNC destroy_component;
unsigned int size;
struct _LIST* head;
};
以下是单个列表节点的定义。这个定义与列表紧密耦合,可以像下面这样移动到列表类型定义中。
struct LIST { COMPARISON_FUNC compare_component; COPY_FUNC copy_component; DESTRUCTION_FUNC destroy_component; unsigned int size; struct _LIST { Object info; struct _LIST* next; struct _LIST* prev; }* head; };
以下定义的 Java 版本涉及使用正在定义的类型名称,而在 C 中这是不可能的。在 C 中,类型名称不能在完成定义之前使用。然而,对于指针来说,这不是问题。无论它们操作的对象的大小如何,它们的大小都不会改变。因此,每当我们在数据类型的描述中使用递归时,它很可能用指针来表示。[9]
struct _LIST {
Object info;
struct _LIST* next;
struct _LIST* prev;
};
typedef struct _LIST* _List;
对 ListIterator 对象执行的所有操作实际上都会作用于底层的 List 对象。现在,我们可以在一个应用程序中拥有多个 List 对象,并且特定的迭代器可以用来遍历其中一个,除了迭代器特定的字段外,我们的结构还包含对封闭的 List 结构的引用。

这类似于 Java 中内部类的实现方式:当转换为 Java 1.0 以便生成 Java 虚拟机字节码时,每个非静态内部类构造函数的签名都会被修改,以便它将封闭实例作为第一个参数接收。一旦构造函数开始控制,此值就会存储在 private 字段中。例如,
public class List implements IListExtended { public List() { ... } ... ... private class Iterator implements ListIterator { private Iterator(int type) { ... } ... } // end of inner class Iterator ... ... } // end of class List
将被转换为
public class List implements IListExtended { public List() { ... } ... ... } // end of class List class List$Iterator implements ListIterator { // This corresponds to the field we named underlying_list!!! private List this$0; List$Iterator(List this$0, int type) { this.this$0 = this$0; ... } // end of constructor(int) ... ... } // end of inner class Iterator
请注意 List$Iterator 类的访问说明符:包级可见,而不是 private。这是因为顶层类不能是 private 或 protected。但是,为什么不使用 public 呢?答案是因为在一个文件中只能有一个 public 类,而恰好是 List 类。
但是,将 Iterator 从 private 提升到包级可见意味着它可以被原本不打算使用的类使用。答案在于合成类名的使用:这样的名称不能在源代码中使用,并且这是由编译器强制执行的。
struct LISTITERATOR {
List underlying_list;
_List ptr;
int index;
int last_op;
};
static _List create_sublist(Object info);
List List_Create(int type, ...) {
int i, array_len;
jmp_buf li_n;
va_list ap;
List_Component_Funcs funcs;
ListIterator itr;
List existing_list;
Object* from_array;
List ret_list = (List) malloc(sizeof(struct LIST));
if (!ret_list) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out of memory...\n");
return(NULL);
} /* end of if(!ret_list) */
ret_list->size = 0;
ret_list->head = NULL;
va_start(ap, type);
switch(type) {
case COPY:
existing_list = va_arg(ap, List);
ret_list->compare_component = existing_list->compare_component;
ret_list->copy_component = existing_list->copy_component;
ret_list->destroy_component = existing_list->destroy_component;
itr = List_ListIterator(existing_list, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
for(; ListIterator_HasNext(itr); )
List_InsertAtEnd(ret_list, existing_list->copy_component(ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n)));
free(itr);
break;
case DEFAULT:
funcs = va_arg(ap, List_Component_Funcs);
ret_list->compare_component = funcs.compare_component;
ret_list->copy_component = funcs.copy_component;
ret_list->destroy_component = funcs.destroy_component;
break;
case FROM_ARRAY:
funcs = va_arg(ap, List_Component_Funcs);
from_array = va_arg(ap, Object*);
array_len = va_arg(ap, int);
ret_list->compare_component = funcs.compare_component;
ret_list->copy_component = funcs.copy_component;
ret_list->destroy_component = funcs.destroy_component;
for (i = 0; i < array_len; i++)
List_InsertAtEnd(ret_list, ret_list->copy_component(from_array[i]));
break;
} /* end of switch(type) */
va_end(ap);
return ret_list;
} /* end of List List_Create(List_Constructor_type, ...) */
void List_Destroy(List* this) {
int size, i;
if (*this == NULL) return;
size = (*this)->size; i = 1;
for (; i <= size; i++)
(*this)->destroy_component(List_RemoveFromFront(*this));
free(*this);
*this = NULL;
} /* end of void List_Destroy(List*) */
Object List_GetFirst(const List this, jmp_buf gfc) /* throws List_Empty */ {
longjmp 是一个函数,它提供跨函数边界的跳转。这样做时,它会利用以前由对 setjmp 函数的调用填充的 jmp_buf 结构。
在某种程度上,longjmp 可以被看作是“激素版的跳转”。除了跳转到其他指令(可能在不同的函数中)之外,它还通过使用 jmp_buf 结构中找到的值来恢复机器状态,以确保程序处于有效状态。因此,以下 longjmp 将跳转到发出相应 setjmp 的位置,并在同时展开运行时堆栈。这样做时,它会在传递给它的第二个参数中返回有关异常情况性质的信息,在本例中,它应该反映出我们想要窥视的列表是一个空列表的事实。
请注意,此展开过程不会撤消对内存或文件系统进行的任何修改;它只是重新建立机器状态,就像之前一样,对主内存和辅助内存内容所做的任何更改都将保留。如果您可能需要更完整的展开,您必须自行负责。
这种行为类似于异常:当抛出的异常没有在当前子程序中处理时,运行时堆栈会被展开,并且控制权将被转移回调用方——这实际上是跨越当前函数边界的跳转——希望它能处理该异常。
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) longjmp(gfc, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
return this->head->info;
} /* end of Object List_GetFirst(const List) */
Object List_GetLast(const List this, jmp_buf glc) /* throws List_Empty */ {
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) longjmp(glc, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
return this->head->prev->info;
} /* end of Object List_GetLast(const List, jmp_buf) */
static _List create_sublist(Object info) {
_List this = (_List) malloc(sizeof(struct _LIST));
if (!this) return NULL;
this->info = info;
this->prev = this->next = this;
return this;
} /* end of _List create_sublist(Object) */
void List_InsertAtEnd(const List this, Object new_item) {
_List new_sublist = create_sublist(new_item);
this->size++;
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) this->head = new_sublist;
else {
_List tail = this->head->prev;
new_sublist->prev = tail;
tail->next = new_sublist;
new_sublist->next = this->head;
this->head->prev = new_sublist;
} /* end of else */
} /* end of void List_InsertAtEnd(const List, Object) */
void List_InsertInFront(const List this, Object new_item) {
_List new_sublist = create_sublist(new_item);
this->size++;
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) this->head = new_sublist;
else {
_List head = this->head;
_List tail = this->head->prev;
this->head = new_sublist;
new_sublist->next = head;
new_sublist->prev = tail;
tail->next = new_sublist;
head->prev = new_sublist;
} /* end of else */
} /* end of void List_InsertInFront(const List, Object) */
Object List_RemoveFromEnd(const List this, jmp_buf rec) /* throws ListEmpty */ {
_List tail;
Object retVal;
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) longjmp(rec, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
this->size--;
tail = this->head->prev;
retVal = tail->info;
if (this->size != 0) {
_List new_tail = tail->prev;
new_tail->next = this->head;
this->head->prev = new_tail;
} else this->head = NULL;
tail->next = tail->prev = NULL;
tail->info = NULL;
free(tail);
return retVal;
} /* end of Object List_RemoveFromEnd(const List, jmp_buf) */
Object List_RemoveFromFront(const List this, jmp_buf rfc) /* throws ListEmpty */ {
_List head;
Object retVal;
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) longjmp(rfc, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
this->size--;
head = this->head;
retVal = head->info;
if (this->size != 0) {
head->prev->next = head->next;
head->next->prev = head->prev;
this->head = head->next;
} else this->head = NULL;
head->next = head->prev = NULL;
head->info = NULL;
free(head);
return retVal;
} /* end of Object List_RemoveFromFront(const List, jmp_buf) */
BOOL List_IsEmpty(const List this) {
if (this->head == NULL) return TRUE;
else return FALSE;
} /* end of BOOL List_IsEmpty(const List) */
int List_Size(const List this) { return this->size; }
Object* List_ToArray(const List this, jmp_buf tac) /* throws ListEmpty */ {
int size = this->size, i;
jmp_buf li_n;
ListIterator itr;
Object* ret_array;
if (size == 0) longjmp(tac, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
ret_array = malloc(sizeof(Object) * size);
if (!ret_array) {
fprintf(stderr, “Out of memory...\n”);
return(NULL);
} /* end of if(!ret_array) */
i = 0; itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
for (; ListIterator_HasNext(itr); i++)
ret_array[i] = ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n);
free(itr);
return ret_array;
} /* end of Object[] List_ToArray(const List, jmp_buf) */
List List_Merge(const List this, const List second_list) {
jmp_buf li_n;
List_Component_Funcs funcs = { this->compare_component, this->copy_component, this->destroy_component };
List ret_list = List_Create(DEFAULT, funcs);
List l1 = this, l2 = second_list;
ListIterator itr;
itr = List_ListIterator(l1, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
for(; ListIterator_HasNext(itr);)
List_InsertAtEnd(ret_list,
ret_list->copy_component(ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n)));
free(itr);
itr = List_ListIterator(l2, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
for(; ListIterator_HasNext(itr);)
List_InsertAtEnd(ret_list,
ret_list->copy_component(ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n)));
free(itr);
return ret_list;
} /* end of List List_Merge(const List, const List) */
ListIterator List_ListIterator(const List this, Iterator_type it_type) {
ListIterator ret_iterator = (ListIterator) malloc(sizeof(struct LISTITERATOR));
if (!ret_iterator) {
fprintf(stderr, “Out of memory...\n”);
return(NULL);
} /* end of if(!ret_iterator) */
ret_iterator->underlying_list = this;
ret_iterator->ptr = this->head;
ret_iterator->last_op = IT_OPERATION_NOOP;
if (it_type == ITERATOR_FORWARD) ret_iterator->index = 0;
else ret_iterator->index = this->size;
return ret_iterator;
} /* end of ListIterator List_ListIterator(const List, Iterator_type) */
void List_InsertAfterFirst(const List this, Object new_item, Object after, jmp_buf iafc)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ {
jmp_buf ins_a_Nth;
执行 setjmp 命令将使用反映其调用时机器状态的值填充传递给它的 jmp_buf 参数。完成时,setjmp 将返回 0。下一步是调用可能导致异常情况的函数(List_InsertAfterNth)。如果一切顺利,控制权将返回到函数调用后的语句,在本例中是返回语句。否则,控制权将返回到发出 setjmp 的地方,并将 List_InsertAfterNth 中调用 longjmp 返回的值作为调用 setjmp 的结果。
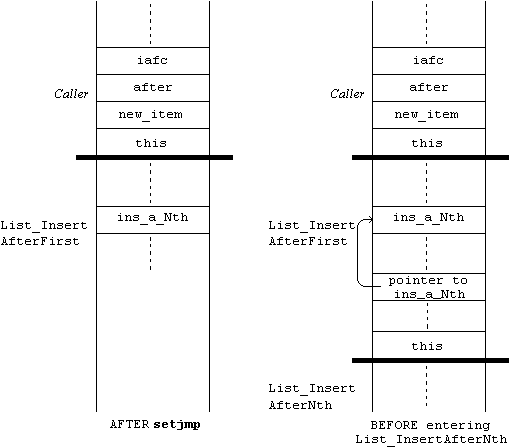
我们可以总结一下发生了什么:
- 通过调用
setjmp记录机器状态并返回 0。 - 调用可能导致异常情况的函数。
- 如果一切正常,则通过
return语句从函数返回有效值。控制流程将像没有进行特殊安排一样进行。否则,通过longjmp函数从函数返回。这样做将(除了展开运行时堆栈)将控制权返回到调用setjmp函数的地方。假装setjmp之前没有被调用过,并将其结果作为longjmp函数的第二个参数中返回的值。
if (setjmp(ins_a_Nth) == EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM)
longjmp(iafc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
List_InsertAfterNth(this, new_item, after, 1, ins_a_Nth);
} /* end of void List_InsertAfterFirst(const List, Object, Object, jmp_buf) */
void List_InsertAfterLast(const List this, Object new_item, Object aft, jmp_buf ialc)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ {
jmp_buf li_a, li_n, li_p;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_BACKWARD);
for(; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); )
if (this->compare_component(aft, ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_p)) == 0) {
ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n);
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
return;
} /* end of if(this->compare_component(aft, …) == 0) */
free(itr);
longjmp(ialc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
} /* end of void List_InsertAfterLast(const List, Object, Object, jmp_buf) */
void List_InsertAfterNth(const List this, Object new_item, Object aft, int n, jmp_buf iaNc)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ {
int index = 0;
jmp_buf li_a, li_n;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
for(; index < n && ListIterator_HasNext(itr); )
if (this->compare_component(aft, ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n)) == 0)
index++;
if (index < n) {
free(itr);
longjmp(iaNc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
} /* end of if (index < n) */
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
} /* end of void List_InsertAfterNth(const List, Object, Object, int, jmp_buf) */
void List_InsertBeforeFirst(const List this, Object new_item, Object before, jmp_buf ibfc)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ {
jmp_buf ins_b_Nth;
if (setjmp(ins_b_Nth) == EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM)
longjmp(ibfc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
List_InsertBeforeNth(this, new_item, before, 1, ins_b_Nth);
} /* end of void List_InsertBeforeFirst(const List, Object, Object, jmp_buf) */
void List_InsertBeforeLast(const List this, Object new_item, Object bef, jmp_buf iblc)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ {
jmp_buf li_a, li_p;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_BACKWARD);
for(; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); )
if (this->compare_component(bef, ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_p)) == 0) {
ListIterator_Add(iterator, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
return;
} /* end of if (this->compare_component…) */
free(itr);
longjmp(iblc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
} /* end of void List_InsertBeforeLast(const List, Object, Object, jmp_buf) */
void List_InsertBeforeNth(const List this, Object new_item, Object before, int n, jmp_buf ibNc)
/* throws NoSuchItem */ {
int index = 0;
jmp_buf li_a, li_n, li_p;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
for(; index < n && ListIterator_HasNext(itr); )
if (this->compare_component(before, ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n)) == 0)
index++;
if (index < n) {
free(itr);
longjmp(ibNc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
} /* end of if (index < n) */
ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_p);
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
} /* end of void List_InsertBeforeNth(const List, Object, Object, int, jmp_buf) */
void List_InsertInAscendingOrder(const List this, Object new_item) {
jmp_buf li_a, li_n, li_p;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_BACKWARD);
for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); ) {
Object next_item = ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_p);
if (this->compare_component(new_item, next_item) < 0) continue;
ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n);
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
return;
} /* end of for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); ) */
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
} /* end of void List_InsertInAscendingOrder(const List, Object) */
void List_InsertInAscendingOrderEx(const List this, Object new_item, COMPARISON_FUNC cmp) {
jmp_buf li_a, li_n, li_p;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_BACKWARD);
for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); ) {
Object next_item = ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_p);
if (cmp(new_item, next_item) < 0) continue;
ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n);
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
return;
} /* end of for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); )*/
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
} /* end of void List_InsertInAscendingOrderEx(const List, Object, COMPARISON_FUNC) */
void List_InsertInDescendingOrder(const List this, Object new_item) {
jmp_buf li_a, li_n, li_p;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_BACKWARD);
for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); ) {
Object next_item = ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_p);
if (this->compare_component(new_item, next_item) > 0) continue;
ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n);
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
return;
} /* end of for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); )*/
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
} /* end of void List_InsertInDescendingOrder(const List, Object) */
void List_InsertInDescendingOrderEx(const List this, Object new_item, COMPARISON_FUNC cmp) {
jmp_buf li_a, li_n, li_p;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_BACKWARD);
for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); ) {
Object next_item = ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_p);
if (cmp(new_item, next_item) > 0) continue;
ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n);
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
return;
} /* end of for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); )*/
ListIterator_Add(itr, new_item, li_a);
free(itr);
} /* end of void List_InsertInDescendingOrderEx(const List, Object, COMPARISON_FUNC) */
int List_RemoveAll(const List this, Object item, jmp_buf rac) /* throws ListEmpty */ {
int i = 0;
jmp_buf li_n, li_r;
ListIterator itr;
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) longjmp(rac, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
for (itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
ListIterator_HasNext(itr); )
if (this->compare_component(item, ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n)) == 0) {
ListIterator_Remove(itr, li_r);
i++;
} /* end of if(->compare_component(item, …) == 0) */
free(itr);
return i;
} /* end of int List_RemoveAll(const List, Object, jmp_buf) */
void List_RemoveFirst(const List this, Object new_item, jmp_buf rfc) /* throws ListEmpty, NoSuchItem */ {
jmp_buf rmv_Nth;
switch (setjmp(rmv_Nth)) {
case 0: break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: longjmp(rfc, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: longjmp(rfc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rmv_Nth)) */
List_RemoveNthFromFront(this, new_item, 1, rmv_Nth);
} /* end of void List_RemoveFirst(const List, Object, jmp_buf) */
void List_RemoveLast(const List this, Object new_item, jmp_buf rlc) /* throws ListEmpty, NoSuchItem */ {
jmp_buf rmv_Nth;
int status = setjmp(rmv_Nth);
switch (status) {
case 0: break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: longjmp(rlc, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: longjmp(rlc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
} /* end of switch(status) */
List_RemoveNthFromEnd(this, new_item, 1, rmv_Nth);
} /* end of void List_RemoveLast(const List, Object, jmp_buf) */
void List_RemoveNthFromEnd(const List this, Object new_itm, int n, jmp_buf rNec)
/* throws ListEmpty, NoSuchItem */ {
int i = 0;
jmp_buf li_p, li_r;
ListIterator itr;
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) longjmp(rNec, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
for (itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_BACKWARD); ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr) && i < n; )
if (this->compare_component(new_itm, ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_p)) == 0)
i++;
if (i == n) {
ListIterator_Remove(itr, li_r);
free(itr);
} else {
free(itr);
longjmp(rNec, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
} /* end of else */
} /* end of void List_RemoveNthFromEnd(const List, Object, int, jmp_buf) */
void List_RemoveNthFromFront(const List this, Object new_itm, int n, jmp_buf rNfc)
/* throws ListEmpty, NoSuchItem */ {
int i = 0;
jmp_buf li_n, li_r;
ListIterator itr;
if (List_IsEmpty(this)) longjmp(rNfc, EXC_LIST_EMPTY);
for (itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_FORWARD); ListIterator_HasNext(itr) && i < n; )
if (this->compare_component(new_itm, ListIterator_Next(itr, li_n)) == 0)
i++;
if (i == n) {
ListIterator_Remove(itr, li_r);
free(itr);
} else {
free(itr);
longjmp(rNfc, EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM);
} /* end of else */
} /* end of void List_RemoveNthFromFront(const List, Object, int, jmp_buf) */
void ListIterator_Destroy(ListIterator* this) {
if (*this == NULL) return;
(*this)->underlying_list = NULL;
free(*this);
*this = NULL;
} /* end of void ListIterator_Destroy(ListIterator) */
BOOL ListIterator_HasNext(const ListIterator this) {
if (this->index == this->underlying_list->size) return FALSE;
else return TRUE;
} /* end of BOOL ListIterator_HasNext(const ListIterator) */
Object ListIterator_Next(const ListIterator this, jmp_buf li_nc) /* throws NoSuchElement */ {
Object retVal;
if (!ListIterator_HasNext(this))
longjmp(li_nc, EXC_ITERATOR_NOSUCHELEMENT);
retVal = this->ptr->info;
this->ptr = this->ptr->next;
this->index++;
this->last_op = IT_OPERATION_NEXT;
return retVal;
} /* end of Object ListIterator_Next(const ListIterator, jmp_buf) */
int ListIterator_NextIndex(const ListIterator this) {
return(this->index);
} /* end of int ListIterator_NextIndex(const ListIterator) */
BOOL ListIterator_HasPrevious(const ListIterator this) {
if (this->index == 0) return FALSE;
else return TRUE;
} /* end of BOOL ListIterator_HasPrevious(const ListIterator) */
Object ListIterator_Previous(const ListIterator this, jmp_buf li_pc) /* throws NoSuchElement */ {
if (!ListIterator_HasPrevious(this))
longjmp(li_pc,EXC_ITERATOR_NOSUCHELEMENT);
this->ptr = this->ptr->prev;
this->index--;
this->last_op = IT_OPERATION_PREVIOUS;
return this->ptr->info;
} /* end of BOOL ListIterator_Previous(const ListIterator, jmp_buf) */
int ListIterator_PreviousIndex(const ListIterator this) {
return (this->index - 1);
} /* end of int ListIterator_PreviousIndex(const ListIterator) */
void ListIterator_Remove(const ListIterator this, jmp_buf li_rc)
/* throws IllegalStateException, UnsupportedOperationException */ {
int index; /* index of the item to be deleted */
_List to_be_deleted;
if (this->last_op != IT_OPERATION_NEXT && this->last_op != IT_OPERATION_PREVIOUS)
longjmp(li_rc, EXC_ITERATOR_ILLEGALSTATE);
switch (this->last_op) {
case IT_OPERATION_NEXT:
to_be_deleted = this->ptr->prev;
index = this->index - 1;
break;
case IT_OPERATION_PREVIOUS:
to_be_deleted = this->ptr;
this->ptr = this->ptr->next;
index = this->index++;
break;
} /* end of switch(this->lastOp) */
this->last_op = IT_OPERATION_REMOVE;
if (index + 1 == this->underlying_list->size) /* if it is the last item in the list */ {
jmp_buf rmv_e_c;
if (setjmp(rmv_e_c) != 0) NO_OP;
List_RemoveFromEnd(this->underlying_list, rmv_e_c);
}
else if (index == 0) /* if it is the first item in the list */ {
jmp_buf rmv_f_c;
if (setjmp(rmv_f_c) != 0) NO_OP;
List_RemoveFromFront(this->underlying_list, rmv_f_c);
} else {
_List next_list = to_be_deleted->next;
_List prev_list = to_be_deleted->prev;
prev_list->next = next_list; next_list->prev = prev_list;
this->underlying_list->destroy_component(to_be_deleted->info);
this->underlying_list->size--;
to_be_deleted->prev = to_be_deleted->next = NULL;
to_be_deleted->info = NULL;
free(to_be_deleted);
}
this->index--;
} /* end of void ListIterator_Remove(const ListIterator, jmp_buf) */
void ListIterator_Add(const ListIterator this, Object new_item, jmp_buf li_ac)
/* throws IllegalState, UnsupportedOperation */ {
_List new_sublist;
if (!ListIterator_HasNext(this))
List_InsertAtEnd(this->underlying_list, new_item);
else if (!ListIterator_HasPrevious(this))
List_InsertInFront(this->underlying_list, new_item);
else {
new_sublist = create_sublist(new_item);
new_sublist->next = this->ptr;
new_sublist->prev = this->ptr->prev;
this->ptr->prev->next = new_sublist;
this->ptr->prev = new_sublist;
this->underlying_list->size++;
}
this->index++;
this->last_op = IT_OPERATION_ADD;
} /* end of void ListIterator_Add(const ListIterator, Object) */
void ListIterator_Set(const ListIterator this, Object new_value, jmp_buf li_sc)
/* throws IllegalArgument, IllegalState, UnsupportedOperation */ {
if (this->last_op == IT_OPERATION_NEXT) {
this->underlying_list->destroy_component(this->ptr->prev->info);
this->ptr->prev->info = new_value;
}
else if (this->last_op == IT_OPERATION_PREVIOUS) {
this->underlying_list->destroy_component(this->ptr->info);
this->ptr->info = new_value;
} else longjmp(li_sc, EXC_ITERATOR_ILLEGALSTATE);
this->last_op = IT_OPERATION_SET;
} /* end of void ListIterator_Set(const ListIterator, Object, jmp_buf) */
在我们的测试程序中,我们提供了两个补充异常概念的简单示例:断言机制和信号。前者用于让编译器在代码中插入运行时控制,因此可以被视为构建正确软件的工具。后者是通知进程已发生事件的通知。换句话说,信号是软件中断——由于计算机、操作系统或系统中某个进程中的某些意外情况——传递给进程。
断言机制和异常处理服务于类似的目的;它们不服务于相同目的。尽管这两种机制都提高了可靠性,但它们通过解决不同的方面来做到这一点:健壮性和正确性。异常处理通过提供从意外情况恢复的能力来实现更健壮的系统,而断言通过检查开发人员做出的断言的有效性来帮助确保正确性。
定义:健壮性与系统对各种情况和可能意外情况的合理反应能力有关。正确性与系统对规范的遵守程度有关,该规范说明了对系统预期行为的要求。
例如,磁盘上缺少数据文件与实现的正确性无关。程序员最好提供一些处理此异常情况的代码。另一方面,传递给子程序的非法参数值很可能是先前错误的结果,例如程序代码中草率的范围检查。
信号在不同的意义上补充异常:当异常是由于当前程序活动[因此是编程语言概念,可以说它是内部的]的意外结果时,信号——操作系统概念——通常是外部的,可能是由于硬件、操作系统或进程造成的。
可以通过一个例子更好地理解异常和信号之间的关系。考虑整数除法。如果除数恰好为零,处理器将生成一个除零中断,该中断将由操作系统进一步传递给语言运行时,作为SIGFPE信号。此信号最终由语言运行时转换为异常,例如ArithmeticException,并传递回包含违规代码的程序,希望该程序能够在该程序中捕获和处理。
信号可以分为三类:程序错误、外部事件和显式请求。错误表示程序执行了某些无效操作,并且操作系统或计算机已检测到该操作。这包括除零、取消引用空指针、取消引用未初始化指针等等。外部事件与 I/O 或与其他进程的通信有关。此类别的示例包括计时器的到期、子进程的终止、停止或挂起进程、将用户终端让给后台作业进行输入或输出等等。显式请求是专门生成信号的库函数调用,例如 abort 和 kill 函数,它们基本上分别生成SIGABRT和SIGKILL。
信号示例包括
SIGINT(中断)- 收到特殊中断键(通常为 Ctrl-C)后,将向进程发送
SIGINT信号。 SIGKILL- 此中断会立即终止进程。无法阻止、处理或忽略此中断。此信号和上一个信号的典型用法是终止已进入无限循环的程序或占用系统资源过多的程序。
SIGTERM- 与
SIGKILL类似,此中断会导致程序终止。但是,与SIGKILL不同,可以阻止、处理或忽略此中断。 SIGSEGV(段错误)- 程序正在尝试读取/写入未为其分配的内存。当使用超出界限的索引值使用数组或取消引用具有正确对齐初始值的未初始化指针时,可能会生成此信号。
SIGILL(非法指令)- 遇到非法或特权指令。由于执行旨在用于不同处理器的二进制文件,可能会引发此类信号,这可以通过在 i386 上运行包含 Pentium-4 指令的可执行文件来举例说明。另一个原因是尝试执行损坏的可执行文件。最后,尝试在用户程序中执行特权指令(例如操纵系统表的指令)也会导致生成此信号。
SIGBUS- 尝试访问无效地址。这可能是由于尝试访问未对齐的数据造成的,这可能发生在取消引用具有随机值的未初始化指针时。
SIGFPE- 发生了通用算术异常。请注意,这不仅限于浮点数,正如其名称可能暗示的那样。它可以是整数除零、溢出等等。
SIGALRM- 每当先前设置的计时器到期时,都会生成此信号。
SIGUSR1和SIGUSR2- 为程序员预留,这些信号可以根据需要进行调整。
当信号发出(或生成)时,它将变为待处理,这意味着它正在等待传递给进程。如果未被进程阻止,这通常需要很短的时间,并且在传递时,将执行某些例程来处理信号。这称为“处理信号”,可能采取的形式是简单地忽略它、接受系统提供的默认操作,或执行用户指定的操作。如果信号被阻止,这意味着它的处理被无限期地推迟到以后的时间,它将保持在(阻塞的)待处理状态。此信号可以稍后解除阻止,由进程处理。

需要注意的是,某些信号既不能被阻止也不能被忽略。事实上,一些信号(例如 SIGKILL)甚至不能使用用户指定的动作来处理。
#include <assert.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "General.h"
#include "Wrappers.h"
#include "ds/ListExtended.h"
#include "ds/ListIterator.h"
void write_to_screen(const List this) {
jmp_buf nxt_c;
ListIterator itr = List_ListIterator(this, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
printf("<%i> <head: ", List_Size(this));
for (; ListIterator_HasNext(itr); ) {
printf("%i", Integer_Value((Integer) ListIterator_Next(itr, nxt_c)));
if (ListIterator_HasNext(itr)) printf(", ");
} /* end of for(; ListIterator_HasNext(itr);) */
printf(" :tail>\n");
} /* end of void write_to_screen(const List) */
void test_extended_removal(const List l) {
int n;
jmp_buf rac, rfc, rlc, rNec, rNfc;
printf("\nTESTING [EXTENDED] REMOVE OPERATIONS\n");
List_RemoveLast(l, Integer_Create(8), rlc);
printf("Removing the last 8...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_RemoveFirst(l, Integer_Create(5), rfc);
printf("Removing the first 5...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_RemoveNthFromEnd(l, Integer_Create(7), 3, rNfc);
printf("Removing the third 7 from the end...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_RemoveNthFromFront(l, Integer_Create(5), 2, rNfc);
printf("Removing the second 5...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
n = List_RemoveAll(l, Integer_Create(6), rac);
printf("Removing all 6's...%i 6's removed.\n", n); write_to_screen(l);
n = List_RemoveAll(l, Integer_Create(7), rac);
printf("Removing all 7's...%i 7's removed.\n", n); write_to_screen(l);
} /* end of void test_extended_removal(const List) */
void test_extended_insertion(const List l) {
jmp_buf iafc, ialc, ibfc, iblc, iaNc, ibNc;
printf("\nTESTING [EXTENDED]INSERT OPERATIONS\n");
List_InsertBeforeFirst(l, Integer_Create(5), Integer_Create(6), ibfc);
printf("Inserting 5 before first 6...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_InsertAfterFirst(l, Integer_Create(5), Integer_Create(6), iafc);
printf("Inserting 5 after first 6...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_InsertBeforeLast(l, Integer_Create(6), Integer_Create(5), iblc);
printf("Inserting 6 before last 5...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_InsertAfterLast(l, Integer_Create(7), Integer_Create(6), ialc);
printf("Inserting 7 after last 6...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_InsertAfterLast(l, Integer_Create(7), Integer_Create(36), ialc);
printf("Inserting 7 after last 36...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_InsertAfterLast(l, Integer_Create(8), Integer_Create(7), ialc);
printf("Inserting 8 after last 7...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_InsertAfterNth(l, Integer_Create(6), Integer_Create(5), 2, iaNc);
printf("Inserting 6 after the second 5...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
List_InsertBeforeNth(l, Integer_Create(6), Integer_Create(5), 3, ibNc);
printf("Inserting 6 before the third 5...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
} /* end of void test_extended_insertion(const List) */
void test_iterators(const List l) {
ListIterator itr;
jmp_buf li_nc, li_pc;
printf("\nTESTING THE FORWARD ITERATOR\n");
itr = List_ListIterator(l, ITERATOR_FORWARD);
for (; ListIterator_HasNext(itr); )
printf("%i ", Integer_Value((Integer) ListIterator_Next(itr, li_nc)));
ListIterator_Destroy(&itr);
printf("\n");
printf("\nTESTING THE BACKWARD ITERATOR\n");
itr = List_ListIterator(l, ITERATOR_BACKWARD);
for (; ListIterator_HasPrevious(itr); )
printf("%i ", Integer_Value((Integer) ListIterator_Previous(itr, li_pc)));
ListIterator_Destroy(&itr);
printf("\n");
} /* end of test_iterators(const List) */
void test_empty_list(const List l) {
jmp_buf gfc, glc, rac, rec, rfc, tac;
assert(List_IsEmpty(l));
printf("Working on the following [empty!] list...\n");
write_to_screen(l);
printf("Trying to get the first item...");
switch(setjmp(gfc)) {
case 0: List_GetFirst(l, gfc); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
} /* end of switch(setjmp(gfc)) */
printf("Trying to get the last item...");
switch(setjmp(glc)) {
case 0: List_GetLast(l, glc); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
} /* end of switch(setjmp(glc)) */
printf("Trying to remove the first [head] item...");
switch(setjmp(rfc)) {
case 0: List_RemoveFromFront(l, rfc); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rfc)) */
printf("Trying to remove the last [tail] item...");
switch(setjmp(rec)){
case 0: List_RemoveFromEnd(l, rec); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rec)) */
printf("Trying to convert to array...");
switch(setjmp(tac)) {
case 0: List_ToArray(l, tac); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
} /* end of switch(setjmp(tac)) */
printf("Trying to remove all 18's...");
switch(setjmp(rac)) {
case 0: List_RemoveAll(l, Integer_Create(18), rac); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rac)) */
printf("\n");
} /* end of void test_empty_list(const List) */
void test_nonempty_list(const List l) {
int n;
jmp_buf iafc, ialc, iaNc, ibfc, iblc, ibNc;
jmp_buf rac, rfc, rlc, rNec, rNfc;
printf("Working on the following list...\n"); write_to_screen(l);
printf("Trying to insert 5 after first 18...");
switch(setjmp(iafc)) {
case 0:
List_InsertAfterFirst(l, Integer_Create(5), Integer_Create(18), iafc); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(iafc)) */
printf("Trying to insert 5 after last 18...");
switch(setjmp(ialc)) {
case 0:
List_InsertAfterLast(l, Integer_Create(5), Integer_Create(18), ialc); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(ialc)) */
printf("Trying to insert 5 after the third 18...");
switch(setjmp(iaNc)) {
case 0:
List_InsertAfterNth(l, Integer_Create(5), Integer_Create(18), 3, iaNc); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(iaNc)) */
printf("Trying to insert 5 before first 18...");
switch(setjmp(ibfc)) {
case 0:
List_InsertBeforeFirst(l, Integer_Create(5), Integer_Create(18), ibfc); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(ibfc)) */
printf("Trying to insert 5 before last 18...");
switch(setjmp(iblc)) {
case 0:
List_InsertBeforeLast(l, Integer_Create(5), Integer_Create(18), iblc); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(iblc)) */
printf("Trying to insert 5 before the third 18...");
switch(setjmp(ibNc)) {
case 0:
List_InsertBeforeNth(l, Integer_Create(5), Integer_Create(18), 3, ibNc); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(ibNc)) */
printf("Trying to remove last 18...");
switch(setjmp(rlc)) {
case 0: List_RemoveLast(l, Integer_Create(18), rlc); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rlc)) */
printf("Trying to remove first 18...");
switch(setjmp(rfc)) {
case 0: List_RemoveFirst(l, Integer_Create(18), rfc); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rfc)) */
printf("Trying to remove third 6...");
switch(setjmp(rNfc)) {
case 0:
List_RemoveNthFromFront(l, Integer_Create(6), 3, rNfc); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rNfc)) */
printf("Trying to remove third 6 from end...");
switch(setjmp(rNec)) {
case 0:
List_RemoveNthFromEnd(l, Integer_Create(6), 3, rNec); break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n"); break;
case EXC_LIST_NOSUCHITEM: printf("No such item!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rNec)) */
printf("Trying to remove all 49's...");
switch(setjmp(rac)) {
case 0:
n = List_RemoveAll(l, Integer_Create(49), rac);
assert(List_RemoveAll(l, Integer_Create(49), rac) == 0);
break;
case EXC_LIST_EMPTY: printf("List is empty!!!\n");
} /* end of switch(setjmp(rac)) */
printf("%i 49's removed.\n", n);
} /* void test_nonempty_list(const List) */
void unexpected_cond(int signal_no) {
if (signal_no != SIGUSR1)
fprintf(stderr, "Unexpected signal: %d\n", signal_no);
else fprintf(stderr, "User signal(SIGUSR1)!\n");
exit(signal_no);
} /* void unexpected_cond(int) */
int main(void) {
int i = 0;
jmp_buf gfc, glc, lac, rec, rfc;
List_Component_Funcs int_funcs =
{ &Integer_CompareIntegers, &Integer_CopyInteger, &Integer_DestroyInteger };
Object obj_array[] =
{ Integer_Create(16), Integer_Create(25), Integer_Create(36), Integer_Create(49) };
Integer* corr_array;
List l1 = List_Create(DEFAULT, int_funcs);
List empty_list = List_Create(COPY, l1);
List l2 = List_Create(FROM_ARRAY, int_funcs, obj_array, 4);
List merged_list;
下一行代码对我们的程序做出了一个断言:l2,它之前是从四个元素的数组中创建的,大小为四个。否则将意味着构造函数或List_Size函数中存在语义错误,必须在List模块上市之前进行纠正。
如果程序状态assert证明我们的断言为假,则会导致中止,并向标准输出写入诊断消息,其中包括断言的“字符串化”版本以及文件名和行号。
示例:在 C 中实现一种方案,确保不会默默地忽略越界索引值。 ... void f(int *iarr, unsigned int size) { ... assert(i * j + k < size && i * j + k >= 0); ... iarr[i * j + k] ... ... } /* end of void f(int*, unsigned int) */ ... f(a, 10); ... f(b, 25); ... ...
当然,这也有代价:每次看到断言,都会花费额外的时间来验证断言,这意味着充满 assert 的代码运行速度会更慢。考虑到生产质量代码不仅需要无错误,而且需要快速,在最终项目中使用 assert 就没有意义了。那么怎么办?我们是否应该移除所有断言(可能会有几十个)——只是为了在需要维护时再放回去?其实不是!在我们的文件中或命令行中定义 NDEBUG 宏作为编译时开关,可以解决这个问题。
assert(List_Size(l2) == 4);
for (; i < 10; i +=2) List_InsertInFront(l1, Integer_Create(i));
for (i = 1; i < 10; i +=2) List_InsertAtEnd(l1, Integer_Create(i));
printf("First list: "); write_to_screen(l1);
printf("Second List: "); write_to_screen(l2);
printf("Merging the lists...\n");
merged_list = List_Merge(l1, l2);
printf("Merged List: "); write_to_screen(merged_list);
另一种处理意外情况的机制:信号。信号最初是 UNIX 的概念,用于通知进程(即正在运行的程序)关于 [通常] 异步事件的发生,例如无效的内存访问或尝试除以零。
除了由计算机的错误检测机制或程序外部的操作触发信号之外,还可以使用 raise 函数显式地“引发”信号。所有这些都会导致相关信号发送到进程。[10] 一旦信号被引发(或以某种方式触发),它需要被处理。这是通过调用信号的处理程序完成的。[11]
这一切都很好,但是我们如何更改程序对特定信号的反应?毕竟,对于同一信号的发生,我们有时可以修改环境并让程序继续运行,而其他时候我们必须简单地终止程序。我们可以通过更改处理程序函数来实现这一点,我们使用 signal 函数来实现。将新的处理程序与信号关联起来,此函数将返回指向先前处理程序的指针。[12] 从现在开始,除非对 signal 的另一次调用再次修改处理程序,否则所有相关信号最终都将在此新函数中处理。
在建立处理程序时,可以将两个特殊值作为第二个参数传递给 signal:SIG_IGN 和 SIG_DFL。前者表示第一个参数中传递的信号将被忽略,而后者表示该信号将接收其默认处理。
if (List_Size(merged_list) != List_Size(l1) + List_Size(l2)) {
void (*previous_handler)(int) = signal(SIGUSR1, &unexpected_cond);
raise(SIGUSR1);
signal(SIGUSR1, previous_handler);
} /* end of if(List_Size(merged_list) != List_Size(l1) + List_Size(l2)) */
printf("First item of the merged list: %i\n", Integer_Value((Integer)List_GetFirst(merged_list, gfc)));
printf("Last item of the merged list: %i\n", Integer_Value((Integer)List_GetLast(merged_list, glc)));
printf("Removing the first and last items in the merged list...\n");
List_RemoveFromEnd(merged_list, rec);
List_RemoveFromFront(merged_list, rfc);
write_to_screen(merged_list);
corr_array = (Integer *) List_ToArray(merged_list, lac);
printf("Corresponding array...\n");
for (i = 0; i < List_Size(merged_list); i++)
printf("[%i] %i ", i, Integer_Value(corr_array[i]));
printf("\n");
test_extended_insertion(merged_list);
test_extended_removal(merged_list);
test_iterators(merged_list);
printf("\nTESTING EXCEPTIONAL CONDITIONS\n");
test_empty_list(empty_list);
test_nonempty_list(merged_list);
return 0;
} /* end of int main(void) */
- gcc –c List.c –ID:/include↵ # 在 Cygwin 中
为了在测试阶段创建可执行文件,我们应该使用以下命令。这将有效地启用断言功能。
- gcc –o Test.exe List_Test.c List.o –lWrappers –ID:/include –LD:/library↵
摆脱程序中的语义错误(或至少希望如此),我们可以停用断言功能。这是通过定义 NDEBUG 宏来完成的。
- gcc –DNDEBUG –o Test.exe List_Test.c List.o –lWrappers –ID:/include –LD:/library↵
通过组合实现代码重用
[edit | edit source]接口
[edit | edit source]#ifndef STACK_H
#define STACK_H
#include <setjmp.h>
#include "General.h"
#define EXC_STACK_EMPTY -41
struct STACK;
typedef struct STACK* Stack;
typedef struct _Obj_funcs {
COMPARISON_FUNC compare_component;
COPY_FUNC copy_component;
DESTRUCTION_FUNC destroy_component;
} Stack_Component_Funcs;
extern Stack Stack_Create(int constructor_type, ...);
extern void Stack_Destroy(Stack*);
extern Object Stack_Peek(const Stack, jmp_buf spc) /* throws StackEmpty */ ;
extern Object Stack_Pop(const Stack, jmp_buf spc) /* throws StackEmpty */ ;
extern void Stack_Push(const Stack, Object);
extern BOOL Stack_IsEmpty(const Stack);
#endif
实现
[edit | edit source]#include <setjmp.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "General.h"
#include "ds/List.h"
#include "ds/Stack.h"
struct STACK { List underlying_list; };
Stack Stack_Create(int type, ...) {
va_list ap;
List_Component_Funcs lst_funcs;
Stack_Component_Funcs funcs;
Stack existing_stack;
Stack ret_stack = (Stack) malloc(sizeof(struct STACK));
if (!ret_stack) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out of memory...\n");
return(NULL);
} /* end of if(!ret_stack) */
va_start(ap, type);
switch(type) {
case COPY:
existing_stack = va_arg(ap, Stack);
ret_stack->underlying_list = List_Create(COPY, existing_stack->underlying_list);
break;
case DEFAULT:
funcs = va_arg(ap, Stack_Component_Funcs);
lst_funcs.compare_component = funcs.compare_component;
lst_funcs.copy_component = funcs.copy_component;
lst_funcs.destroy_component = funcs.destroy_component;
ret_stack->underlying_list = List_Create(DEFAULT, lst_funcs);
break;
} /* end of switch(type) */
va_end(ap);
return ret_stack;
} /* end of Stack Stack_Create(int, ...) */
void Stack_Destroy(Stack* this) {
if (*this == NULL) return;
List_Destroy(&(*this)->underlying_list);
free(*this);
*this = NULL;
} /* end of void Stack_Destroy(Stack*) */
Object Stack_Peek(const Stack this, jmp_buf sp_c) /* throws Stack_Empty */ {
Object res;
if (List_IsEmpty(this->underlying_list))
longjmp(sp_c, EXC_STACK_EMPTY);
由于当控制到达此点时,我们已经确保堆栈不为空——通过检查底层列表,如之前的 if 语句中——因此传递缓冲区没有意义,缓冲区用于传递有关任何问题的的信息。因此,我们将 NULL 作为第二个参数传递。
res = List_GetFirst(this->underlying_list, NULL);
return res;
} /* end of Object Stack_Peek(const Stack, jmp_buf) */
Object Stack_Pop(const Stack this, jmp_buf sp_c) /* throws StackEmpty */ {
jmp_buf rfc;
Object res;
if (setjmp(rfc) == EXC_LIST_EMPTY)
longjmp(sp_c, EXC_STACK_EMPTY);
res = List_RemoveFromFront(this->underlying_list, rfc);
return res;
} /* end of Object Stack_Pop(const Stack, jmp_buf) */
void Stack_Push(const Stack this, Object new_item) {
List_InsertInFront(this->underlying_list, new_item);
} /* end of void Stack_Push(const Stack, Object) */
BOOL Stack_IsEmpty(const Stack this) {
return(List_IsEmpty(this->underlying_list));
} /* end of BOOL Stack_IsEmpty(const Stack) */
注释
[edit | edit source]- ↑ ISO C 要求
EOF被定义为一个负的整型常量。 - ↑ 这当然可以通过移除错误处理来避免,但这会导致更大的灾难。
- ↑ 本质上,异常处理是由操作系统提供的服务。我们还应该添加编译器支持,它会生成相关的代码。
- ↑ 首先确保你执行了名为 vcvars32.bat 的批处理文件,该文件位于 Microsoft Visual C/C++ 编译器的 bin 子目录中,然后在 Visual Studio .NET 命令提示符中发出命令
- cl /w /FeExecName.exe CsourceName.c /link /SAFESEH:NO↵
- ↑ TIB 代表线程信息块,它保存特定于当前线程的信息。
- ↑ 所有 Win32 进程的第一个分区对用户不可访问。尝试读取或写入此分区(其大小可能因操作系统而异)会导致访问冲突,并导致进程终止。这对于处理 C 中的
NULL指针操作是一个相当实用的工具:如果NULL宏被定义为零或第一个分区范围内的任何地址值,则在没有编译器干扰的情况下,任何尝试解引用NULL指针最终都会导致访问冲突。 - ↑ 注意,我们优先选择清晰度而不是简洁。这个代码块当然可以写得更简洁。
- ↑ 你早就知道它会依赖于机器!毕竟,作为状态信息的一部分,我们需要存储一堆寄存器值,而这些值在不同的架构之间是不同的(在数量和大小上)。
- ↑ 这支持我们对句柄作为智能指针的看法。
- ↑ 注意它与抛出异常的相似之处。
- ↑ 非常类似于 catch 块的主体。
- ↑
SIGUSR1的默认处理程序会做什么?
