分形/复平面迭代/柯尼希斯坐标
外观
< 分形
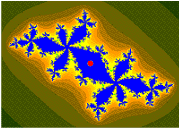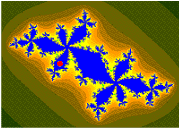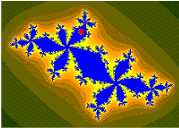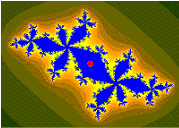
柯尼希斯[1] 坐标[2] 用于有限吸引(非超吸引)点(循环)[3][4] 的吸引盆。
- 一个至少为二阶的有理映射 f
- 一个不动点
- 乘子 的不动点是
- 不动点是吸引的,但不是超吸引的
- = 在函数 下不动点零的吸引盆。换句话说,包含不动点的分量的内部 = 由所有在 f 下的轨道收敛到 0 的点组成的开集。
它由归一化迭代近似
它可以用公式定义
函数 f 在局部上与模型线性映射共轭[5]
二次一维多项式 fc(z)=z²+c 的动力学
// Created by inigo quilez - iq/2013
// License Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
//
//-----------------https://www.shadertoy.com/view/MdX3zN-------------------------------------------
//
// Dynamics for quadratic 1D polynomials fc(z)=z²+c
//
// * Orange: the Fatou set Kc.
// * Black: the Julia set Jc.
// * Checkerboard distortion: the Boettcher map phi(z).
// * Checkerboard shadowing: the gradient of the Green's function, log|phi(z)|
// * Blue: the two fixed points.
// * Green, the period 2 fixed points.
// * White: c
// * Yellow: the Koening coordinates
//
// Some theory:
//
// * c (white) belongs to Kc (orange), for these are all connected Julia sets.
//
// * When both fixed points (blue) are in Jc but not in Kc, or in other words, when both points
// are repeling (derivative of fc(z) is bigger than one), c does not belong to the Mandelbrot
// set's main cardioid, but to bulbs of higher period. In that case Kc (orange) is made of several
// branches (as many as the period of the bul)
//
// * When one of the two fixed points (blue dots) is inside Kc, meanins it is attractive (derivative
// of fc(z) < 1), then c belongs to the main cardiod of the Mandelbrot set, and Kc is a single piece
// shape.
//
// * When the period 2 fixed points are always repelling (belong to Jc, not to Kc) except for the sets
// that have c belonging to the period-2 bulb of the Mandelbrot set. In those cases, the green dots
// become attractive and sit inside the orange area Kc.
//
// * The Koening coordinates can only been seen when c belongs to the main cariod{{typo help inline|reason=similar to cardiod|date=July 2023}} of the Madelbrot set
//
//------------------------------------------------------------
// complex number operations
vec2 cadd( vec2 a, float s ) { return vec2( a.x+s, a.y ); }
vec2 cmul( vec2 a, vec2 b ) { return vec2( a.x*b.x - a.y*b.y, a.x*b.y + a.y*b.x ); }
vec2 cdiv( vec2 a, vec2 b ) { float d = dot(b,b); return vec2( dot(a,b), a.y*b.x - a.x*b.y ) / d; }
vec2 csqrt( vec2 z ) { float m = length(z); return sqrt( 0.5*vec2(m+z.x, m-z.x) ) * vec2( 1.0, sign(z.y) ); }
vec2 conj( vec2 z ) { return vec2(z.x,-z.y); }
vec2 cpow( vec2 z, float n ) { float r = length( z ); float a = atan( z.y, z.x ); return pow( r, n )*vec2( cos(a*n), sin(a*n) ); }
//------------------------------------------------------------
float argument( in vec2 p )
{
float f = atan( p.y, p.x );
if( f<0.0 ) f += 6.2831;
f = f/6.2831;
return f;
}
float grid( in vec2 p )
{
vec2 q = 16.0*p;
vec2 r = fract( q );
float fx = smoothstep( 0.05, 0.06, r.x ) - smoothstep( 0.94, 0.95, r.x );
float fy = smoothstep( 0.05, 0.06, r.y ) - smoothstep( 0.94, 0.95, r.y );
return 0.5 + 0.5*mod( floor(q.x)+floor(q.y), 2.0 );
}
float cross( vec2 a, vec2 b )
{
return a.x*b.y - a.y*b.x;
}
bool isInTriangle( in vec2 p, in vec2 a, in vec2 b, in vec2 c )
{
vec3 di = vec3( cross( b - a, p - a ),
cross( c - b, p - b ),
cross( a - c, p - c ) );
return all(greaterThan(di,vec3(0.0)));
}
float distanceToSegment( vec2 a, vec2 b, vec2 p )
{
vec2 pa = p - a;
vec2 ba = b - a;
float h = clamp( dot(pa,ba)/dot(ba,ba), 0.0, 1.0 );
return length( pa - ba*h );
}
vec3 circle( vec3 bcol, vec3 col, in vec2 a, in vec2 b )
{
float rr = 0.04;
vec3 res = mix( bcol, col, 1.0 - smoothstep( rr-0.01, rr, length(a-b) ) );
float f = smoothstep( rr-0.01, rr, length(a-b) ) - smoothstep( rr, rr+0.01, length(a-b) );
return mix( res, vec3(0.0), f );
}
//------------------------------------------------------------
void mainImage( out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord )
{
vec2 uv = fragCoord.xy/iResolution.xy;
vec2 p = -1.0 + 2.0*uv;
p.x *= iResolution.x/iResolution.y;
float at = mod( (iGlobalTime+.5)/5.0, 8.0 );
vec2 c = vec2(-0.800, 0.100);
c = mix( c, vec2( 0.280,-0.490), smoothstep(0.0,0.1,at) );
c = mix( c, vec2(-0.500,-0.500), smoothstep(1.0,1.1,at) );
c = mix( c, vec2(-0.160, 0.657), smoothstep(2.0,2.1,at) );
c = mix( c, vec2(-0.650, 0.100), smoothstep(3.0,3.1,at) );
c = mix( c, vec2(-0.114, 0.650), smoothstep(4.0,4.1,at) );
c = mix( c, vec2(-0.731, 0.166), smoothstep(5.0,5.1,at) );
c = mix( c, vec2(-0.100,-0.660), smoothstep(6.0,6.1,at) );
c = mix( c, vec2(-0.800, 0.100), smoothstep(7.0,7.1,at) );
// get the 2 fixed points
vec2 one = vec2( 1.0, 0.0 );
vec2 fix1_1 = 0.5*( one + csqrt( one - 4.0*c ) );
vec2 fix1_2 = 0.5*( one - csqrt( one - 4.0*c ) );
vec2 fix2_1 = -(csqrt(-4.0*c-3.0*one)+one)/2.0;
vec2 fix2_2 = (csqrt(-4.0*c-3.0*one)-one)/2.0;
vec2 fix2_3 = -(csqrt( one-4.0*c)-one)/2.0;
vec2 fix2_4 = (csqrt( one-4.0*c)+one)/2.0;
vec2 z = p;
vec2 dz = vec2( 1.0, 0.0 );
vec2 ph = z;
vec2 gr = vec2( log(length(z)), atan(z.y,z.x) );
float t = 0.0;
for( int i=0; i<512; i++ )
{
if( dot(z,z)>10000.0 ) continue;
t += 1.0;
// derivative
dz = 2.0*cmul( z, dz );
// point
z = cmul(z,z) + c;
vec2 a = cdiv(z,z-c);
float s = pow( 0.5, t );
// phi
ph = cmul( ph, cpow(a, s) );
// green
gr.x += log(length(a)) * s;
float aa = atan(a.y,a.x);
if( isInTriangle( z, vec2(0.0), fix1_2, c ) )
{
aa -= sign(aa)*2.0*3.14159;
}
gr.y += aa * s;
}
vec3 col = vec3(1.0,0.65,0.10);
if( t<511.0 )
{
float s = pow( 0.5, t );
vec2 phib = cpow( z, s );
float phiR = length( phib );
float greenR = log(length(z)) * s;
float greenI = argument(z*s);
float d = log( length(z) ) * length(z) / length(dz);
vec2 gradG = -conj(cmul( dz, conj(z) ));
float n = t/50.0;
float sn = -log2(abs(greenR))/50.0;
col = vec3( 0.6 + 0.4*dot(normalize(-gradG),vec2(0.707)) );
col *= vec3( grid( ph ) );
col *= vec3(1.0)*clamp(d*50.0,0.0,1.0);
}
else
{
z = p;
float t = 0.0;
for( int i=0; i<200; i++ )
{
if( length(z-fix1_2)>0.001 )
{
z = cmul(z,z) + c;
t += 1.0;
}
}
vec2 fix = fix1_2;
if( length(2.0*fix1_1)<1.0 ) fix=fix1_1;
if( length(2.0*fix)<1.0 )
{
vec2 ph = cdiv( z - fix, cpow(2.0*fix,t) );
float g = log(length(ph));
float l = 1.0 - 0.1*smoothstep( 0.7, 0.71, sin(48.0*g) );
col += 0.1*(abs(g));
ph = 1.0*vec2( length(ph), atan(ph.y,ph.x)/3.14 );
col *= l;
}
}
// color depending of attractive/repulsive fixed point
col = circle( col, vec3(1.0,1.0,1.0), p, c );
vec3 col2 = vec3(0.0,1.0,0.0);
col = circle( col, col2, p, fix2_1 );
col = circle( col, col2, p, fix2_2 );
col = circle( col, col2, p, fix2_3 );
col = circle( col, col2, p, fix2_4 );
vec3 col1 = vec3(0.0,0.7,1.0);
col = circle( col, col1, p, fix1_1 );
col = circle( col, col1, p, fix1_2 );
fragColor = vec4( col, 1.0 );
}
- ↑ 麦克图尔数学史档案中的加布里埃尔·柯尼希斯传记
- ↑ Shadertoy 示例
- ↑ G. Koenigs, Recherches sur les intégrales de certaines équations fonctionnelles, Annales École Normale Supérieure, 1(3) (1884), Supplément, 3-41.
- ↑ 伊尼戈·奎莱斯图像和教程
- ↑ 周期性法图分量的分类和结构。哈佛大学数学系高级荣誉论文,作者:本杰明·多齐尔。导师:莎拉·科赫 2012 年 3 月 19 日
- ↑ 维基百科中的柯尼希斯函数
- ↑ 科尼希斯函数的幂级数展开










