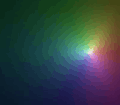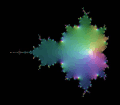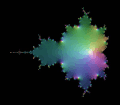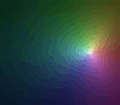
分形/复平面迭代/曼德博集内部
外观
< 分形
这本书展示了如何为绘制参数平面[1](曼德博集[2])的复二次多项式[3]编写不同的算法。
人们可以在参数平面上找到不同类型的点/集[4]。
此页面介绍曼德博集的内部点[5]。
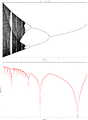
The “capture-time algorithm” is a natural counterpart for points inside the set to the “escape-time algorithm”. Given some desired tolerance, the orbit P is generated for each point c ∈ C until some point in the orbit is closer than to some previous point in the orbit. The number of iterations needed for this to occur is mapped to a color and displayed at the pixel corresponding to c. Adam Cunningham[6]
-
整个集合
-
迷你曼德博集
-
实二次映射
数学公式 :[7]
其中
表示 f 对 z 的一阶导数
另请参阅
JPBotelho 的 HLSL 代码[10]
Shader "Fractals/Coloring Techniques/Escape-Time"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_Iter ("Iterations", Range(0, 250)) = 100
_Dividend ("Dividend", Range (0, 0.5)) = 15
_Zoom ("Zoom", Range (0.1, 1000)) = 0.65
_Position ("Offset", Vector) = (0.4, 0, 0, 0)
_Background ("Background", Color) = (0, 0.25, 1, 0)
_Origin ("Origin", Color) = (0, 0, 0, 0)
}
SubShader
{
Cull Off ZWrite Off ZTest Always
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
#include "Complex.cginc"
#include "FractalOperations.cginc"
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
int _Iter;
fixed _Zoom;
fixed _Dividend;
float2 _Position;
fixed4 _Background;
fixed4 _Origin;
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = v.uv;
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
float x0 = (ClampScaleX(i.uv) + _Position.x) / _Zoom;
float y0 = (ClampScaleY(i.uv) + _Position.y) / _Zoom;
float2 z = float2(x0, y0);
float2 c = float2(x0, y0);
int iteration = 0;
float l = 0;
while (IsBounded(z, 40) && iteration < _Iter)
{
l += log (cabs(2 * z));
z = cmul(z, z);
z += c;
iteration++;
}
l /= iteration;
if (l > 0)
return _Background;
float3 color = tanh(l >= 0 ?
float3(0, 0.7 * log(1 + l), log(1 + l)) :
3 * float3(_Origin.x-l, _Origin.y-l * 0.1, _Origin.z));
return float4(color + _Dividend, 1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
CustomEditor "FractalEditor"
}

# Hypercomputing the Mandelbrot Set? by Petrus H. Potgieter February 1, 2008
n=1000; # For an nxn grid
m=50; # Number of iterations
c=meshgrid(linspace(-2,2,n))\ # Set up grid
+i*meshgrid(linspace(2,-2,n))’;
x=zeros(n,n); # Initial value on grid
for i=1:m
x=x.^2+c; # Iterate the mapping
endfor
imagesc(min(abs(x),2.1)) # Plot monochrome, absolute
# value of 2.1 is escape
点的颜色
- 与 z 在最终迭代时的值成正比。
- 显示周期性吸引子的内部水平集。
bof60 的图像在“分形之美”一书的第 60 页。bof 第 63 页描述了该方法。它仅用于曼德博集的内部点。
点的颜色与
- 其轨道与原点[11][12]
- 迭代过程中 z 取得的最小值[13]
- 阐明原点(临界点)的迭代在集合内部最接近原点的距离
- “视频帧的每个像素都代表一个特定的复数 c = a + ib。对于每个连续帧 n,z(c,n) := z(c, n-1)^2 + c 的大小显示为每个这些点 c 的灰度强度值:大小较大的点更白,大小较小的点更暗。随着 n 从 1 增加到 256,曼德博集外部的点快速饱和为纯白色,而曼德博集内部的点在较暗的强度之间振荡。” Brian Gawalt[14]
距离的水平集是距离相同的点的集合[15]
if (Iteration==IterationMax)
/* interior of Mandelbrot set = color is proportional to modulus of last iteration */
else { /* exterior of Mandelbrot set = black */
color[0]=0;
color[1]=0;
color[2]=0;
}
- 代码片段 : 来自 Gnofract4d 的 fractint.cfrm[16]
bof60 {
init:
float mag_of_closest_point = 1e100
loop:
float zmag = |z|
if zmag < mag_of_closest_point
mag_of_closest_point = zmag
endif
final:
#index = sqrt(mag_of_closest_point) * 75.0/256.0
}
另请参阅
- Bof61
-
动画
-
2D
-
3D

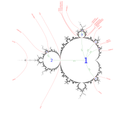
曼德博集的双曲分量的周期是临界轨道的极限集的周期。
计算周期的算法
- 直接从动力学平面上的临界点 z = 0.0 的迭代中检测周期
- "快速而肮脏" 算法:检查是否 ,则将 c 点用颜色 n 着色。这里 n 是吸引轨道的周期,eps 是围绕吸引点的圆的半径 = 数值计算的精度。
- "当正确实现时,基于区间算术的方法能够找到相当大的 n 的所有 n 周期循环。"(ZBIGNIEW GALIAS)[17]
- 弗洛伊德循环查找算法[18]
- 蜘蛛算法
- 原子域,BOF61
- 周期检测
内部检测
[edit | edit source]如果下面所有内容都为真,则像素以高概率为内部[19]
- 像素标记为内部(黑色)
- 所有周围像素标记为内部(黑色)
- 所有黑色像素具有相同的周期
内部坐标和倍增器映射
[edit | edit source]
克劳德·海兰德-艾伦的算法
- 检查 c
- 当 c 在曼德勃罗集之外时
- 现在放弃
- 或使用外部坐标
- 当 c 不在外部(在内部或边界上)时:对于每个周期 p,从 1 开始递增
- 使用 牛顿法 在一个复变数中找到周期点 z0,使得 fp(z0,c)=z0
- 通过评估 fp 在 z0 处的关于 z 的一阶导数来找到 b
- 如果 |b|≤1,则返回 b,否则继续执行下一个 p
- 当 c 在曼德勃罗集之外时
计算
[edit | edit source]对于周期:[23]
- 1 到 3 可以使用显式方程[24]
- >3 必须使用数值方法找到
周期 1
[edit | edit source]从 边界方程 开始
c+(w/2)^2-w/2=0;
并对 w 求解
(%i1) eq1:c+(w/2)^2-w/2=0;
2
w w
(%o1) -- - - + c = 0
4 2
(%i2) solve(eq1,w);
(%o2) [w = 1 - sqrt(1 - 4 c), w = sqrt(1 - 4 c) + 1]
(%i3) s:solve(eq1,w);
(%o3) [w = 1 - sqrt(1 - 4 c), w = sqrt(1 - 4 c) + 1]
(%i4) s:map(rhs,s);
(%o4) [1 - sqrt(1 - 4 c), sqrt(1 - 4 c) + 1]
所以
w = w(c) = 1.0 - csqrt(1.0-4.0*c)
周期 2
[edit | edit source]w = 4.0*c + 4;
周期 3
[edit | edit source]
它可以使用 Maxima CAS 求解
(%i1) e1:c^3 + 2*c^2 - (w/8-1)*c + (w/8-1)^2 = 0;
3 2 w w 2
(%o1) c + 2 c + (1 - -) c + (- - 1) = 0
8 8
(%i2) solve(e1,w);
(%o2) [w = (- 4 sqrt((- 4 c) - 7) c) + 4 c + 8, w = 4 sqrt((- 4 c) - 7) c + 4 c + 8]
数值近似
[edit | edit source]complex double AproximateMultiplierMap(complex double c, int period, double eps2, double er2)
{
complex double z; // variable z
complex double zp ; // periodic point
complex double zcr = 0.0; // critical point
complex double d = 1;
int p;
// first find periodic point
zp = GivePeriodic( c, zcr, period, eps2, er2); // Find periodic point z0 such that Fp(z0,c)=z0 using Newton's method in one complex variable
// Find w by evaluating first derivative with respect to z of Fp at z0
if ( cabs2(zp)<er2) {
z = zp;
for (p=0; p < period; p++){
d = 2*z*d; /* first derivative with respect to z */
z = z*z +c ; /* complex quadratic polynomial */
}}
else d= 10000; //
return d;
}
另请参阅
内部角
[edit | edit source]
雷纳托·丰塞卡的方法:[25] "集合中的点 c 被赋予等于参数的色调
(适当缩放,以便最终得到 0 - 255 范围内的数字)。数字 z_nmax 是在 z 的序列中计算的最后一个数字。
另请参阅
Fractint
[edit | edit source]Fractint:颜色参数:INSIDE=ATAN
通过确定最后一个迭代值相对于实轴的角度(以度为单位)以及使用绝对值来确定颜色。此功能应与 periodicity=0[26] 一同使用
内部射线
[edit | edit source]从内部射线上的双曲参数到抛物线参数[27]
-
内部射线和外部射线
-
倍增器映射和内部射线
-
内部射线和外部射线
当 变化且 保持不变,则 沿着 内部射线 移动。[28] 它用作曼德勃罗集内部的路径。
double complex Give_c(double t, double r, int p)
{
/*
input:
InternalRadius = r in [0,1]
InternalAngleInTurns = t in range [0,1]
p = period
output = c = complex point of 2D parameter plane
*/
complex double w = 0.0;
complex double c = 0.0;
t = t*2*M_PI; // from turns to radians
// point of unit circle
w = r* cexp(I*t);
// map circle to component
switch (p){
case 1: c = (2.0*w - w*w)/4.0; break;
case 2: c = (w -4.0)/ 4.0; break;
}
return c;
}
/* find c in component of Mandelbrot set
uses complex type so #include <complex.h> and -lm
uses code by Wolf Jung from program Mandel
see function mndlbrot::bifurcate from mandelbrot.cpp
http://www.mndynamics.com/indexp.html
*/
double complex GiveC(double InternalAngleInTurns, double InternalRadius, unsigned int period)
{
//0 <= InternalRay<= 1
//0 <= InternalAngleInTurns <=1
double t = InternalAngleInTurns *2*M_PI; // from turns to radians
double R2 = InternalRadius * InternalRadius;
double Cx, Cy; /* C = Cx+Cy*i */
switch ( period ) {
case 1: // main cardioid
Cx = (cos(t)*InternalRadius)/2-(cos(2*t)*R2)/4;
Cy = (sin(t)*InternalRadius)/2-(sin(2*t)*R2)/4;
break;
case 2: // only one component
Cx = InternalRadius * 0.25*cos(t) - 1.0;
Cy = InternalRadius * 0.25*sin(t);
break;
// for each period there are 2^(period-1) roots.
default: // safe values
Cx = 0.0;
Cy = 0.0;
break; }
return Cx+ Cy*I;
}
// draws points to memory array data
int DrawInternalRay(double InternalAngleInTurns, unsigned int period, int iMax, unsigned char data[])
{
complex double c;
double InternalRadius;
double RadiusStep; // between radius of points
int i; // number of point to draw
RadiusStep = 1.0/iMax;
for(i=0;i<=iMax;++i){
InternalRadius = i * RadiusStep;
c = GiveC(InternalAngleInTurns, InternalRadius, period);
DrawPoint(c,data);
}
return 0;
}
示例:角度为 1/6 的主心形的内部射线。
内部角
射线的半径
单位圆内部半径的点
将点 映射到参数平面
对于 ,这是主心形线的方程式。
内部曲线
[edit | edit source]当 保持不变而 变化时, 沿内部曲线移动。
/* find c in component of Mandelbrot set
uses complex type so #include <complex.h> and -lm
uses code by Wolf Jung from program Mandel
see function mndlbrot::bifurcate from mandelbrot.cpp
http://www.mndynamics.com/indexp.html
*/
double complex GiveC(double InternalAngleInTurns, double InternalRadius, unsigned int period)
{
//0 <= InternalRay<= 1
//0 <= InternalAngleInTurns <=1
double t = InternalAngleInTurns *2*M_PI; // from turns to radians
double R2 = InternalRadius * InternalRadius;
double Cx, Cy; /* C = Cx+Cy*i */
switch ( period ) {
case 1: // main cardioid
Cx = (cos(t)*InternalRadius)/2-(cos(2*t)*R2)/4;
Cy = (sin(t)*InternalRadius)/2-(sin(2*t)*R2)/4;
break;
case 2: // only one component
Cx = InternalRadius * 0.25*cos(t) - 1.0;
Cy = InternalRadius * 0.25*sin(t);
break;
// for each period there are 2^(period-1) roots.
default: // safe values
Cx = 0.0;
Cy = 0.0;
break;
}
return Cx+ Cy*I;
}
// draws points to memory array data
int DrawInternalCurve(double InternalRadius , unsigned int period, int iMax, unsigned char data[])
{
complex double c;
double InternalAngle; // in turns = from 0.0 to 1.0
double AngleStep;
int i;
// int iMax =100;
AngleStep = 1.0/iMax;
for (i=0; i<=iMax; ++i) {
InternalAngle = i * AngleStep;
c = GiveC(InternalAngle, InternalRadius, period);
DrawPoint(c,data);
}
return 0;
}
分量的中心
[edit | edit source]更多教程和代码
[edit | edit source]
教程
- 在 Basic 中查看 Mandelbrot Dazibao
- 在 Java 中查看 Evgeny Demidov
- 在 C 中查看 Linas Vepstas
- 在 C++ 中查看 Wolf Jung 页面,
- 在 Factor 程序 由 Slava Pestov
- 在 Gnuplot 中查看 T.Kawano 的教程
- 在 Lisp (Maxima) 中查看
- 在 Octave 中查看 华夏公益教科书 或由 Christopher Wellons 编写的另一个版本
- 如何手工绘制曼德勃罗集
- 不同语言的对比
- 计算机语言基准游戏 : 使用 ≈12 个有缺陷的基准测试,比较 ≈30 种编程语言在 4 种不同的操作系统/机器组合中的性能。
- rosettacode
- Fractal Benchmark 在 Ruby、Io、PHP、Python、Lua、Java、Perl、Applescript、TCL、ELisp、Javascript、OCaml、Ghostscript 和 C 中 由 Erik Wrenholt
- 在 PDL、IDL、MATLAB、Octave、C 和 FORTRAN77 中 由 Xavier Calbet
- ASCI 图 :[29]
- 3D
-
这是图像 "Mandel zoom 03 seehorse.jpg" DEM 的 3D 版本
-
半 3D 超复数曼德勃罗分形。使用 Mandelbulber 0.80 渲染。
参考文献
[edit | edit source]- ↑ 维基百科中的参数平面
- ↑ 维基百科中的曼德勃罗集
- ↑ 维基百科中的复二次多项式
- ↑ reenigne 博客 : mandelbrot-set-taxonomy
- ↑ 由 A Cunningham 展示曼德勃罗集的内部结构(包含 Python 3 程序和代码)
- ↑ 由 Adam Cunningham 展示曼德勃罗集的内部结构
- ↑ 2013 年 10 月 4 日由 Didier Gonze 编写的逻辑斯蒂方程
- ↑ 由 janthor 编写的 Lyapunov 指数和曼德勃罗集
- ↑ Anders Sandberg 的图片
- ↑ github 仓库 JPBotelho: Fractal-Megacollection(Unity 的 HLSL 着色器)
- ↑ Fractint : 杂项选项和算法
- ↑ Java™ Number Cruncher: The Java Programmer's Guide to Numerical Computing 由 Ronald Mak
- ↑ Firefly 应用程序帮助 由 Terry W. Gintz
- ↑ 曼德勃罗振荡 由 Brian Gawalt
- ↑ Fractint 文档 由 Noel Giffin
- ↑ gnofract4d
- ↑ Zbigniew Galias 著《使用区间方法对电子电路中的周期轨道进行严格研究》
- ↑ Milan 绘制的曼德勃罗集
- ↑ fractalforums.org : 使用级数逼近确定最佳跳过迭代次数
- ↑ Claude Heiland-Allen 著《曼德勃罗集内部坐标》
- ↑ Claude Heiland-Allen 著《内部距离渲染实践》
- ↑ math.stackexchange 问题:如何测试点是否属于周期为 n 的曼德勃罗集瓣?
- ↑ Robert P. Munafo 著《Brown 方法》,2003 年 9 月 22 日。
- ↑ Robert P. Munafo 著《精确坐标》,2003 年 9 月 22 日。
- ↑ Renato Fonseca 著《曼德勃罗集》
- ↑ fractint 颜色参数
- ↑ Yi-Chiuan Chen 和 Tomoki Kawahira 著《沿着内部射线的双曲参数到抛物线参数》
- ↑ 维基百科中的内部射线
- ↑ ASCII 图形