GLSL 编程/Unity/球体的软阴影

本教程涵盖了球体的软阴影。
它是关于照明的几个教程之一,它超出了 Phong 反射模型,Phong 反射模型是一种局部照明模型,因此不考虑阴影。介绍的技术在任何网格上渲染单个球体的软阴影,并且与 Orion Sky Lawlor 提出的技术有些相关(参见“进一步阅读”部分)。着色器可以扩展以渲染少量球体的阴影,但代价是渲染性能;然而,它不能轻松地应用于任何其他类型的阴影投射器。潜在的应用包括电脑弹球游戏(其中球体通常是唯一需要软阴影的物体,也是唯一应该在所有其他物体上投射动态阴影的物体)、具有球形主角的电脑游戏(例如“弹珠狂热”)、仅由球体组成的可视化(例如行星可视化、小核、原子或分子的球形模型等)或可以填充球体并受益于软阴影的测试场景。
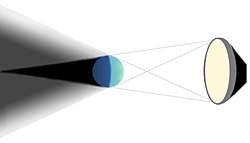

虽然方向光源和点光源会产生硬阴影,但任何面积光源都会产生软阴影。对于所有真实光源也是如此,特别是太阳以及任何灯泡或灯具。从阴影投射器后面的某些点,光源的任何部分都不可见,阴影是均匀的黑暗:这就是本影。从其他点,光源的或多或少部分是可见的,因此阴影或多或少是完整的:这就是半影。最后,有一些点可以从那里看到光源的整个区域:这些点位于阴影之外。
在许多情况下,阴影的柔和度主要取决于阴影投射器和阴影接收器之间的距离:距离越大,阴影越柔和。这在艺术中是一个众所周知的现象;例如,请参考右边的卡拉瓦乔的绘画。

我们将近似计算表面上一个点的阴影,当半径为的球体在S处(相对于表面点)遮挡了半径为的球形光源在L处(同样相对于表面点);参见左边的图。
为此,我们考虑一个方向为T的切线,该切线与球体相切并经过表面点。此外,选择该切线位于L和S所跨越的平面内,即平行于左边图的视角平面。关键的观察结果是,光源中心与该切线的最小距离与表面点的阴影量直接相关,因为它决定了从表面点可见的光源区域有多大。更准确地说,我们需要一个带符号的距离(如果切线与球体在L的同侧,则为正,否则为负),以确定表面点是在本影内 (),在半影内 (),还是在阴影之外 ()。
为了计算,我们考虑L和S之间的角度以及T和S之间的角度。这两个角度之间的差值是L和T之间的角度,它与的关系为
.
因此,到目前为止,我们有
我们可以使用以下公式计算T和S之间的角度
.
因此
.
对于L和S之间的角度,我们使用叉积的一个特性
.
所以
.
总的来说,我们有
我们目前所做的近似处理影响不大;更重要的是它不会产生渲染伪影。如果性能是一个问题,我们可以更进一步地使用 arcsin(x) ≈ x;也就是说,我们可以使用
这避免了所有三角函数;然而,它确实引入了渲染伪像(特别是如果镜面高光在面向光源的半影中)。这些渲染伪像是否值得性能提升需要针对每种情况做出决定。
接下来我们看看如何根据 计算阴影程度 。当 从 减少到 , 应该从 0 增加到 1。换句话说,我们想要在 的 -1 到 1 值之间进行平滑过渡。实现这一点可能最有效的方法是使用内置 GLSL 函数 smoothstep(a,b,x) = t*t*(3-2*t) 提供的 Hermite 插值,其中 t=clamp((x-a)/(b-a),0,1)
虽然这不是 和 之间基于物理的关系的特别好的近似,但它仍然能正确地体现基本特征。
此外, 应该为 0,如果光线方向 L 与 S 方向相反;也就是说,如果它们的点积为负。这个条件有点棘手,因为它会导致 L 和 S 正交的平面上出现明显的间断。为了使这种间断平滑,我们再次可以使用 smoothstep 来计算改进的值
此外,如果点光源比遮挡球更靠近表面点,我们必须将 设置为 0。这也有点棘手,因为球形光源可能会与投射阴影的球体相交。一个避免过于明显的伪影(但无法处理完全相交问题)的解决方案是
在定向光源的情况下,我们只需设置 。然后,指定无阴影照明的级别的项 应该乘以光源的任何照明。(因此,环境光不应乘以该因子。)如果计算多个阴影投射器的阴影,则对于每个光源,必须组合所有阴影投射器的项 。常见的方法是将它们相乘,尽管这可能不准确(特别是当阴影相交时)。
实现
[edit | edit source]该实现计算lightDirection 和sphereDirection 向量的长度,然后继续处理归一化向量。这样,这些向量的长度只需要计算一次,我们甚至可以避免一些除法,因为我们可以使用归一化向量。以下是片段着色器的关键部分
// computation of level of shadowing w
vec3 sphereDirection = vec3(_SpherePosition - position);
float sphereDistance = length(sphereDirection);
sphereDirection = sphereDirection / sphereDistance;
float d = lightDistance
* (asin(min(1.0,
length(cross(lightDirection, sphereDirection))))
- asin(min(1.0, _SphereRadius / sphereDistance)));
float w = smoothstep(-1.0, 1.0, -d / _LightSourceRadius);
w = w * smoothstep(0.0, 0.2,
dot(lightDirection, sphereDirection));
if (0.0 != _WorldSpaceLightPos0.w) // point light source?
{
w = w * smoothstep(0.0, _SphereRadius,
lightDistance - sphereDistance);
}
使用asin(min(1.0, ...)) 确保asin 的参数在允许的范围内。
完整着色器代码
[edit | edit source]完整的源代码定义了用于投射阴影的球体和光源半径的属性。所有值都应该在世界坐标中。对于定向光源,光源半径应以弧度表示(1 弧度 = 180° / π)。设置投射阴影的球体的位置和半径的最佳方法是一个简短的脚本,该脚本应该附加到使用着色器的所有接收阴影的对象,例如
@script ExecuteInEditMode()
var occluder : GameObject;
function Update () {
if (null != occluder) {
renderer.sharedMaterial.SetVector("_SpherePosition",
occluder.transform.position);
renderer.sharedMaterial.SetFloat("_SphereRadius",
occluder.transform.localScale.x / 2.0);
}
}
此脚本有一个公共变量occluder,应该设置为投射阴影的球体。然后它设置了以下着色器的属性_SpherePostion 和_SphereRadius(该着色器应该附加到与脚本相同的接收阴影的对象)。
Shader "GLSL shadow of sphere" {
Properties {
_Color ("Diffuse Material Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_SpecColor ("Specular Material Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_Shininess ("Shininess", Float) = 10
_SpherePosition ("Sphere Position", Vector) = (0,0,0,1)
_SphereRadius ("Sphere Radius", Float) = 1
_LightSourceRadius ("Light Source Radius", Float) = 0.005
}
SubShader {
Pass {
Tags { "LightMode" = "ForwardBase" }
// pass for ambient light and first light source
GLSLPROGRAM
// User-specified properties
uniform vec4 _Color;
uniform vec4 _SpecColor;
uniform float _Shininess;
uniform vec4 _SpherePosition;
// center of shadow-casting sphere in world coordinates
uniform float _SphereRadius;
// radius of shadow-casting sphere
uniform float _LightSourceRadius;
// in radians for directional light sources
// The following built-in uniforms (except _LightColor0)
// are also defined in "UnityCG.glslinc",
// i.e. one could #include "UnityCG.glslinc"
uniform vec3 _WorldSpaceCameraPos;
// camera position in world space
uniform mat4 _Object2World; // model matrix
uniform mat4 _World2Object; // inverse model matrix
uniform vec4 _WorldSpaceLightPos0;
// direction to or position of light source
uniform vec4 _LightColor0;
// color of light source (from "Lighting.cginc")
varying vec4 position;
// position of the vertex (and fragment) in world space
varying vec3 varyingNormalDirection;
// surface normal vector in world space
#ifdef VERTEX
void main()
{
mat4 modelMatrix = _Object2World;
mat4 modelMatrixInverse = _World2Object; // unity_Scale.w
// is unnecessary because we normalize vectors
position = modelMatrix * gl_Vertex;
varyingNormalDirection = normalize(vec3(
vec4(gl_Normal, 0.0) * modelMatrixInverse));
gl_Position = gl_ModelViewProjectionMatrix * gl_Vertex;
}
#endif
#ifdef FRAGMENT
void main()
{
vec3 normalDirection = normalize(varyingNormalDirection);
vec3 viewDirection =
normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos - vec3(position));
vec3 lightDirection;
float lightDistance;
float attenuation;
if (0.0 == _WorldSpaceLightPos0.w) // directional light?
{
attenuation = 1.0; // no attenuation
lightDirection = normalize(vec3(_WorldSpaceLightPos0));
lightDistance = 1.0;
}
else // point or spot light
{
lightDirection = vec3(_WorldSpaceLightPos0 - position);
lightDistance = length(lightDirection);
attenuation = 1.0 / lightDistance; // linear attenuation
lightDirection = lightDirection / lightDistance;
}
// computation of level of shadowing w
vec3 sphereDirection = vec3(_SpherePosition - position);
float sphereDistance = length(sphereDirection);
sphereDirection = sphereDirection / sphereDistance;
float d = lightDistance
* (asin(min(1.0,
length(cross(lightDirection, sphereDirection))))
- asin(min(1.0, _SphereRadius / sphereDistance)));
float w = smoothstep(-1.0, 1.0, -d / _LightSourceRadius);
w = w * smoothstep(0.0, 0.2,
dot(lightDirection, sphereDirection));
if (0.0 != _WorldSpaceLightPos0.w) // point light source?
{
w = w * smoothstep(0.0, _SphereRadius,
lightDistance - sphereDistance);
}
vec3 ambientLighting =
vec3(gl_LightModel.ambient) * vec3(_Color);
vec3 diffuseReflection =
attenuation * vec3(_LightColor0) * vec3(_Color)
* max(0.0, dot(normalDirection, lightDirection));
vec3 specularReflection;
if (dot(normalDirection, lightDirection) < 0.0)
// light source on the wrong side?
{
specularReflection = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
// no specular reflection
}
else // light source on the right side
{
specularReflection = attenuation * vec3(_LightColor0)
* vec3(_SpecColor) * pow(max(0.0, dot(
reflect(-lightDirection, normalDirection),
viewDirection)), _Shininess);
}
gl_FragColor = vec4(ambientLighting
+ (1.0 - w) * (diffuseReflection + specularReflection),
1.0);
}
#endif
ENDGLSL
}
Pass {
Tags { "LightMode" = "ForwardAdd" }
// pass for additional light sources
Blend One One // additive blending
GLSLPROGRAM
// User-specified properties
uniform vec4 _Color;
uniform vec4 _SpecColor;
uniform float _Shininess;
uniform vec4 _SpherePosition;
// center of shadow-casting sphere in world coordinates
uniform float _SphereRadius;
// radius of shadow-casting sphere
uniform float _LightSourceRadius;
// in radians for directional light sources
// The following built-in uniforms (except _LightColor0)
// are also defined in "UnityCG.glslinc",
// i.e. one could #include "UnityCG.glslinc"
uniform vec3 _WorldSpaceCameraPos;
// camera position in world space
uniform mat4 _Object2World; // model matrix
uniform mat4 _World2Object; // inverse model matrix
uniform vec4 _WorldSpaceLightPos0;
// direction to or position of light source
uniform vec4 _LightColor0;
// color of light source (from "Lighting.cginc")
varying vec4 position;
// position of the vertex (and fragment) in world space
varying vec3 varyingNormalDirection;
// surface normal vector in world space
#ifdef VERTEX
void main()
{
mat4 modelMatrix = _Object2World;
mat4 modelMatrixInverse = _World2Object; // unity_Scale.w
// is unnecessary because we normalize vectors
position = modelMatrix * gl_Vertex;
varyingNormalDirection = normalize(vec3(
vec4(gl_Normal, 0.0) * modelMatrixInverse));
gl_Position = gl_ModelViewProjectionMatrix * gl_Vertex;
}
#endif
#ifdef FRAGMENT
void main()
{
vec3 normalDirection = normalize(varyingNormalDirection);
vec3 viewDirection =
normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos - vec3(position));
vec3 lightDirection;
float lightDistance;
float attenuation;
if (0.0 == _WorldSpaceLightPos0.w) // directional light?
{
attenuation = 1.0; // no attenuation
lightDirection = normalize(vec3(_WorldSpaceLightPos0));
lightDistance = 1.0;
}
else // point or spot light
{
lightDirection = vec3(_WorldSpaceLightPos0 - position);
lightDistance = length(lightDirection);
attenuation = 1.0 / lightDistance; // linear attenuation
lightDirection = lightDirection / lightDistance;
}
// computation of level of shadowing w
vec3 sphereDirection = vec3(_SpherePosition - position);
float sphereDistance = length(sphereDirection);
sphereDirection = sphereDirection / sphereDistance;
float d = lightDistance
* (asin(min(1.0,
length(cross(lightDirection, sphereDirection))))
- asin(min(1.0, _SphereRadius / sphereDistance)));
float w = smoothstep(-1.0, 1.0, -d / _LightSourceRadius);
w = w * smoothstep(0.0, 0.2,
dot(lightDirection, sphereDirection));
if (0.0 != _WorldSpaceLightPos0.w) // point light source?
{
w = w * smoothstep(0.0, _SphereRadius,
lightDistance - sphereDistance);
}
vec3 diffuseReflection =
attenuation * vec3(_LightColor0) * vec3(_Color)
* max(0.0, dot(normalDirection, lightDirection));
vec3 specularReflection;
if (dot(normalDirection, lightDirection) < 0.0)
// light source on the wrong side?
{
specularReflection = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
// no specular reflection
}
else // light source on the right side
{
specularReflection = attenuation * vec3(_LightColor0)
* vec3(_SpecColor) * pow(max(0.0, dot(
reflect(-lightDirection, normalDirection),
viewDirection)), _Shininess);
}
gl_FragColor = vec4((1.0 - w) * (diffuseReflection
+ specularReflection), 1.0);
}
#endif
ENDGLSL
}
}
// The definition of a fallback shader should be commented out
// during development:
// Fallback "Specular"
}
总结
[edit | edit source]恭喜!我希望您成功渲染了一些漂亮的软阴影。我们已经了解了
- 什么是软阴影以及什么是半影和本影。
- 如何计算球体的软阴影。
- 如何实现计算,包括使用 JavaScript 编写的脚本,该脚本根据另一个
GameObject设置一些属性。
进一步阅读
[edit | edit source]如果您还想了解更多信息
- 关于着色器代码的其余部分,您应该阅读 “平滑镜面高光”部分。
- 关于软阴影的计算,您应该阅读 Orion Sky Lawlor 的出版物:“插值友好型软阴影贴图”,发表在 2006 年计算机图形和虚拟现实大会论文集,第 111-117 页。预印本可在 网上 获得。
























