
这个公式是伪装的毕达哥拉斯定理。

如果你看一下下一部分的图表,它应该很清楚原因。一个直角三角形的斜边为单位长度,则该三角形角度为  的正弦和余弦只是两条较短边的长度。所以将它们平方并相加得到斜边的平方,即 1 的平方,即 1。
的正弦和余弦只是两条较短边的长度。所以将它们平方并相加得到斜边的平方,即 1 的平方,即 1。
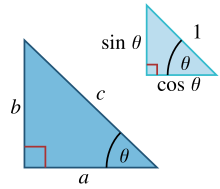 显示角度 θ 的正弦和余弦的相似直角三角形
显示角度 θ 的正弦和余弦的相似直角三角形
更详细地说......在一个边长为  ,斜边为
,斜边为  的直角三角形中,三角学 (Soh-Cah-Toa) 确定了边
的直角三角形中,三角学 (Soh-Cah-Toa) 确定了边  和斜边之间的角度
和斜边之间的角度  的正弦和余弦为
的正弦和余弦为

由此得出

其中最后一步应用了毕达哥拉斯定理。正弦和余弦之间的这种关系有时被称为基本毕达哥拉斯三角恒等式。[1] 在相似三角形中,边的比率是相同的,无论三角形的大小如何,并且取决于角度。因此,在图中,斜边为单位长度的三角形的对边长度为  ,邻边长度为
,邻边长度为  ,以斜边为单位。
,以斜边为单位。
正弦和余弦都不会超过 1,并且其中一个越接近 1,另一个就必须越接近 0。我们可以从两个方面看到这一点
- 它直接从公式中得出。当正弦平方或余弦平方越接近 1 时,留给另一个的值就会减少。
- 从几何上可以看出。斜边是 1,并且比其他两条边都长。当一条边越接近 1 时,另一条边就必须越接近 0。
如果  ,那么  等于多少?
根据毕达哥拉斯恒等式,

如果  ,那么 ,那么

求解  ,在等式两边同时加上 ,在等式两边同时加上  ,得到 ,得到
 
在最后一步,我们需要在  和  之间做出选择。我们选择正值,因为从三角形中可以看出,  是正数。
|
在之前的练习中,我们要求你绘制点  ,你应该得到一个圆 - 嗯,你应该是这样做的。
,你应该得到一个圆 - 嗯,你应该是这样做的。
对于你绘制的每个点,都有一个直角三角形,其坐标为  。
。
该三角形的斜边是从  到
到  的线。斜边的平方长度为
的线。斜边的平方长度为  ,因为这个值是 1,所以斜边长度为 1。因此,你绘制的每个点都距离点
,因为这个值是 1,所以斜边长度为 1。因此,你绘制的每个点都距离点  1 个单位,这就是所有点都位于半径为 1、中心为
1 个单位,这就是所有点都位于半径为 1、中心为  的圆上的必要条件。
的圆上的必要条件。
事实上,你绘制的点都满足  。这是因为
。这是因为  并且
并且  。如果你绘制的是满足
。如果你绘制的是满足  的点,你会得到一个半径为
的点,你会得到一个半径为  的圆。
的圆。





























