结构生物化学/有机化学/有机官能团/羰基


羰基是一个官能团,由一个双键连接到一个氧原子的碳原子组成。连接到氧原子的碳可以与不同的原子形成单键。连接到碳原子的原子将其区别于酮、醛、羧酸、酯或酰胺。
[1]==羰基化合物的命名法==
1、羧酸的命名
The functional carboxylic acid is called a carboxyl group. In systematic nomenclature, a carboxylic acid is named by replacing the last alphabet "e" with "oic acid." For instance, a two carbon alkane is called ethane and two carboxylic acid is ethanoic acid. Notice that a carboxylic acid with 6 or less carbons are usually known by their common names. ( methanoic acid = formic acid, ethanoic acid = acetic acid, propanoic acid= propionic acid, butanoic acid= butyric acid, pentanoic acid= valeric acid, hexanoic acid= caproic acid)
2、酰卤的命名
Acyl halides have a halide in place of the -OH group in a carboxylic acid. Acyl halides are named by replacing "-ic acid" in the acid name with "-yl halide" (eg; -yl chloride, -yl bromide, -yl flouride etc). If acid has a name with "-carboxylic acid," then replace "carboxylic acid with "-carbonyl halide" (e.g. -carbonyl chloride, -carbonyl bromide, -carbonyl fluoride)
3、酸酐
An acid anhydride is formed by two molecules of carboxylic acid reacting with each other to lose one water molecule. An anhydride is a symmetrical anhydride if the two reacting acid molecules are the same. If two reacting acid molecules are different then they are going to from a mixed anhydride. Symmetrical anhydrides are named by replacing "acid" in acid name with "anhydride." Mixed anhydrides are named by stating the names of both acids in alphabetical order then followed by "anhydride."
4、酯的命名
If there is an -OR group in place of the -OH group of a carboxylic acid, the name of the group attached to the carboxyl oxygen should be
首先说明醇部分,然后说明酸的名称,用“-ate”代替“-ic acid”。
Salts of carboxylic acids are named in the same way. The cation is named first then name the acid with replacing "-ic acid" by "-ate" Notice that cyclic esters are called lactones. Their common names are derived from the common name of the carboxylic acid, which designates the length of the carbon chain, and a Greek letter to indicate the carbon to which the carboxyl oxygen is attached.
5、酰胺的命名
An amide has an -NH2, -NHR, or -NR2 group in place of -OH group of a carboxylic acid. They are named by replacing "-oic acid", "-ic acid", or "-ylic acid" of the acid name with "-amide." If a substituent is bonded to the nitrogen, the name of the substituent should be stated first (if there is more than one substituent bonded to the nitrogen, they should be stated alphabetically), then state the name of the amide. The name of each substituent is preceded by capital N to indicate that the substituent is bonded to a nitrogen. Cyclic amides are called lactams. Their nomenclature is similar to that of lactones.
| 化合物 | 醛 | 酮 | 羧酸 | 酯 | 酰胺 |
| 结构 | 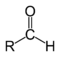 |
 |

|
每个化合物特性的详细信息都可以在其特定的页面上找到。
氧的电负性远大于碳,因此电子密度在氧附近较高,在碳附近较低。这会产生一个偶极矩,其中氧带负电荷,碳带相同大小的正电荷。这种电荷分布使碳成为亲电试剂,而氧成为由此产生的亲核试剂。
每个羰基化合物的反应性取决于直接连接到α碳的基团。这是因为由于该基团的电子捐赠而形成的共振稳定结构。共振结构的贡献越强,羰基的稳定性就越强。这方面的一个例子可以在羧酸中看到,羧酸在去质子化后会产生一个简并结构,从而增加质子的酸性。肽键异常强,由于酰胺电子到α碳的共振贡献,具有更多的sp2,平面杂化。这大大降低了肽键的反应性,因此需要大量能量或蛋白酶来催化该键。羰基本身是非常稳定的键,其形成能通常很高。这使得羰基在有机合成中的形成在热力学上非常有利,通常羰基键作为最终产物的形成将驱动反应形成。
羰基具有一个短而强且极性的双键。由于氧的电负性以及孤对电子,其双键的反应性与烯烃的双键截然不同。羰基碳也吸电子,因为它非常靠近高电负性的氧。醛和酮的极化也改变了物理常数。羰基的极化是其沸点高于具有相似分子量的烃的原因。羰基的极性导致较小的分子在水中完全混溶。具有超过六个碳的羰基化合物被认为是大的,在溶液中不溶。化合物越大,其烃链就越大,分子越疏水,因此其溶解度就会下降。
诱导效应要注意,碳的亲电性高度依赖于附近的原子以及直接与之结合的原子。例如,羧酸的羰基碳不会像酮的羰基碳那样亲电,因为存在共振稳定。另一方面,乙酰氯(碳与一个R-基团结合,双键连接到氧,然后连接到氟),将具有更亲电的羰基碳,因为电负性氯将增加碳的诱导正偶极。亲电性在化学反应中起着关键作用,亲电性较低的羰基碳没有那么容易反应。

在生物系统中,羰基化合物可以通过醇的氧化形成。有机化学中的氧化反应是指添加电负性原子或从分子中去除氢的过程。这种氧化的一个例子包括氧化剂烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸 (NAD+) 氧化乙醇。NAD+ 由一个吡啶环、两个核糖分子和杂环腺嘌呤组成。当在酶醇脱氢酶存在的情况下,1-氘乙醇的两种对映异构体与 NAD+ 反应时,发现生物化学氧化是立体特异性的(NAD+ 仅去除 1-氘乙醇中连接到 C1 原子的氢。 [2] 与上面描述的 1-氘乙醇氧化类似,其他醇可以生物化学氧化以形成羰基。另一个例子包括甲醇氧化成甲醛。 [2]
在'HNMR 光谱中,醛化合物具有非常独特的化学位移,它似乎出现在 9-10 ppm 之间。这意味着醛甲酰氢也受到非常强的屏蔽。醛 C2 氢也略微屏蔽,因为羰基的氧吸电子。在酮中,情况也很类似。α-氢也经历这种屏蔽;其化学位移在 2-2.8 ppm 之间。
醛和酮的碳-13 NMR 光谱是相同的,因为它与参与羰基的碳的化学位移相同。由于该碳与氧结合,它将在约 200 ppm 的较低场出现。与羰基碳相邻的碳也被屏蔽(就像'HNMR 中的氢一样)。距离羰基碳更远的碳屏蔽程度较低。
所有羰基化合物的红外吸收带都在 1760-1665 cm-1 区域,这是由于 C=O 键的伸缩振动。通常,羰基具有高强度和狭窄的区域,使其可用于诊断目的。
| 范围 | 化合物类型 | 例如 |
|---|---|---|
| 1750-1735 cm-1 | 饱和脂肪族酯 | CH3-CH2-COOR |
| 1740-1720 cm-1 | 饱和脂肪族醛 | CH3-CH2-COH |
| 1730-1715 cm-1 | α,β-不饱和酯 | R'(R")C-CH-COOR |
| 1715 cm-1 | 饱和脂肪族酮 | CH3-CH2-CO-CH2-CH3 |
| 1710-1665 cm-1 | α,β-不饱和醛和酮 | R'(R")C-CH-COH |
- ↑ Bruice,Paula Yurkanis.有机化学第六版,Pearson Education,Inc. 纽约。2010
- ↑ a b 无效的
<ref>标签;没有为名为Schore的参考文献提供文本 - ↑ “红外:羰基化合物。”红外:羰基化合物。TurnKey Linux,2008 年。网络。2012 年 11 月 20 日。<http://orgchem.colorado.edu/Spectroscopy/irtutor/carbonylsir.html>.
